14
EN
EBS Ink-Jet Systeme
20111028#4.2
EN
Text Files and Print Pa-
rameters
How to Create a Text to be
Printed?
Regular Text
See figure
Insert texts in the text edit line in the
edit window.
Use a mouse and the following key-
board keys to edit a text as standard
and as you do in other Windows®
applications:
¡
to move the cursor horizon-
tally to the right,
¢
to move the cursor horizon-
tally to the left,
Y¡
to move the cursor horizon-
tally to the right and high-
light the text,
Y¢
move the cursor horizon-
tally to the left and highlight
the text,
Delete
to delete one character to
the right of the cursor,
BackSpace
to delete one character to
the left of the cursor,
Home
to move the cursor to the
beginning of the text,
End
to move the cursor to the
end of the text.
!
You can type in up to 1300 charac-
ters in one text.
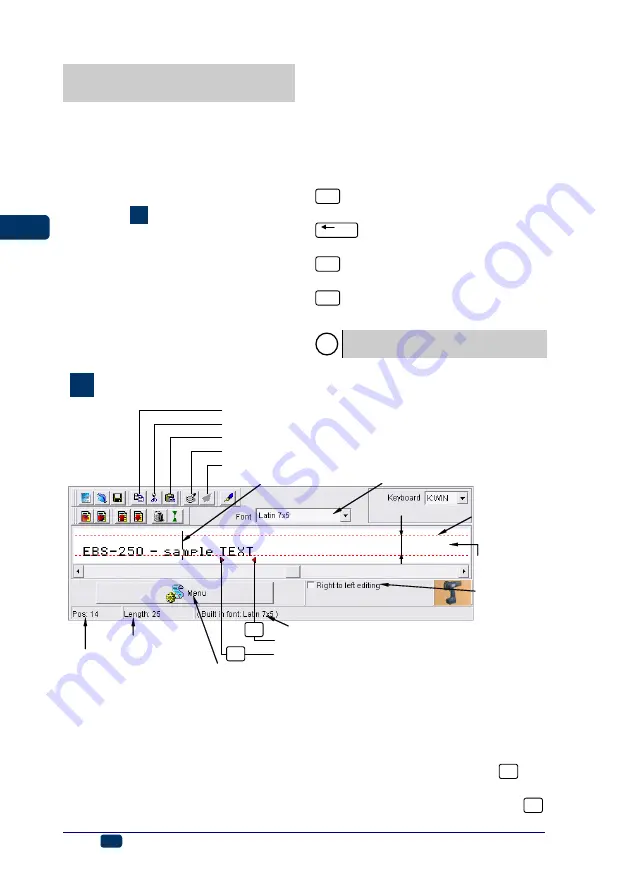
G
Text edit window
cursor position in the text
sample position of the cursor
total length of text
printer font type at the current cursor position
paste a text from the clipboard (
Ctrl+V
)
preview a print
preview other prints
cut and copy a text to the clipboard (
Ctrl+X
)
copy a text to the clipboard (
Ctrl+C
)
text edit line
end-of-monospaced-text marker
beginning-of-monospaced-text marker
F2
F1
maximum text
height
H
max
H
max
change font
MENU button (corresponds to the right mouse button)
character
insertion mode
Changing Proportional Spacing
and Monospacing
Proportional fonts are used to insert
texts as standard. This means that each
letter takes a space proportional to the
character width. For example, a letter
W
takes more space than a letter
I
.
When monospaced fonts are used,
the character width does not depend
on the character. In other words, each
character has the same width. The
beginning of a monospaced piece of
text is usually marked with the
F1
key
and the end of a monospaced piece
of text is usually marked with the
F2





























