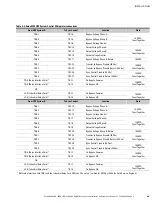
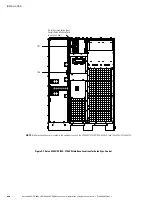
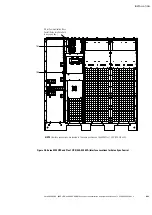
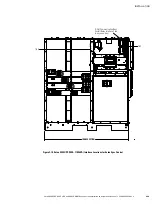
Eaton 9390 UPS, 9395 UPS, and 9395 SSBM Sync Control Installation and Operation Manual
S
P-164000052 Rev 2
www.eaton.com/powerquality
4-1
Chapter 4
Operating Instructions
This chapter describes the operation of the Eaton Sync Control with a UPS or SSBM
system.
4.1
Startup for UPS Systems Equipped with an Eaton Sync Control
Startup and operational checks must be performed by an authorized Eaton Customer
Service Engineer, or the warranty terms as specified on page 5-1 become void. This
service is offered as part of the sales contract for the UPS. Contact service in advance
(usually a two-week notice is required) to reserve a preferred startup date.
4.2
Understanding Eaton Sync Control Operation
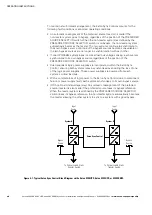
The Eaton Sync Control maintains critical load synchronization of either two separate
single Eaton 9390 UPS systems, two separate single Eaton 9395 UPS systems, or
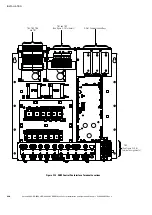
two separate 9395 SSBM systems. See Figure 4‐1 for a typical block diagram of the
system. Synchronization of the UPS systems facilitates the uninterrupted transfer of
customer loads from one load bus to another by means of downstream, dual-source,
solid-state transfer switches. Enable the automatic synchronization action of the
Eaton Sync Control by pressing the LOAD SYNC ENABLE pushbutton on the front of
the panel. When enabled, the LOAD SYNC ENABLE pushbutton illuminates.
The Eaton Sync Control panel provides a three-phase synchronization reference to
each system. Each system uses this reference to regulate the inverter phase
relationship so that the two system outputs can maintain synchronization with each
other. To establish the three-phase synchronization reference, each system provides
bypass sensing voltage and output (critical load) bus voltage to the Eaton Sync
Control.
Under normal operating conditions, bypass sensing voltage from each system is
provided back to its inverter through the Eaton Sync Control. As long as the two
bypass sources feeding System-A and System-B are available and in phase, each
system remains in synchronization with its own bypass source and the two systems
remain in synchronization with each other. If the two bypass sources become out of
phase with each other (>0.1 Hz apart) or one or both sources become unavailable, the
Eaton Sync Control provides a new three-phase synchronization reference to the
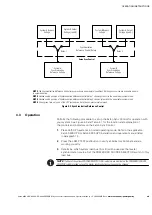
non-master system as determined by the PREFERRED SOURCE SELECTOR switch.
The non-master system's new synchronization reference is provided by the Eaton
Sync Control from the output (critical load) bus of the system designated as master
by the PREFERRED SOURCE SELECTOR switch. See Figure 4‐2 for a diagram of the
synchronization reference control operation.
When the two bypass sources regain availability and synchronization, the Eaton Sync
Control provides the non-master system with its own bypass sensing voltage as a
synchronization reference. Before resynchronization occurs, a 15-second preset time
delay ensures the two bypass sources maintain acceptable synchronization.
Figure