EPQ DataNode Series User’s Guide
3
Operation
3-9
Detecting Oscillatory Transients
These types of disturbances are captured as waveshape
faults. The waveshape fault triggering algorithm essential-
ly compares the samples for each cycle to the correspond-
ing samples from the previous cycle. If the samples differ
by more than Threshold tolerance for a length of time
exceeding Window percent of the power frequency cycle,
a waveshape fault is registered. This algorithm is very
sensitive to small deviations and allows triggering on
waveform deviations that might not cause peak detection-
based algorithms to trigger. The actual algorithm is more
involved than this, but this is the basic idea. A trigger
occurs when one or more voltage channels meets the trig-
gering criteria.
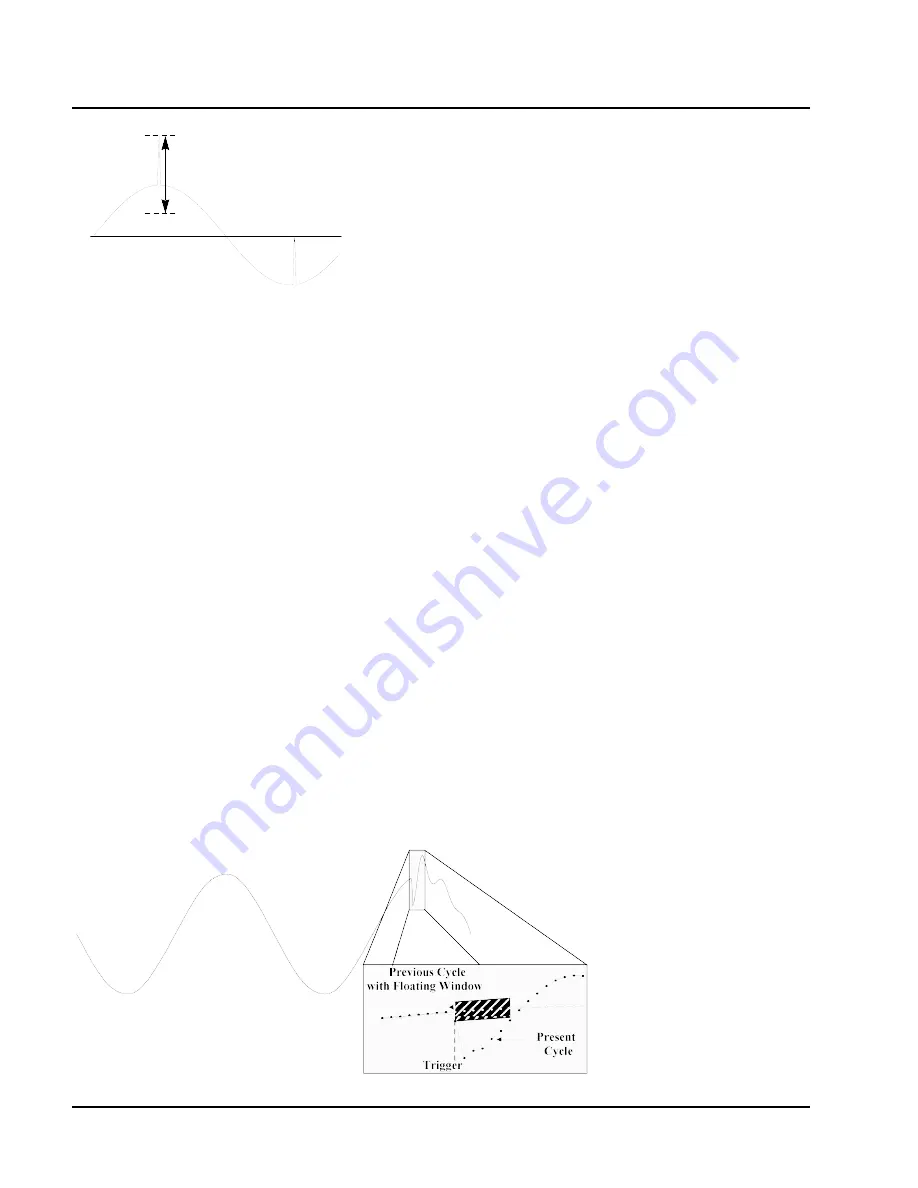
Figure 3.7 below illustrates the "floating window" algo-
rithm used for waveshape fault detection. This window
can be visualized as sliding along the waveform, precisely
one cycle behind the previous sample point, vi. The
height of the window defines a maximum allowable volt-
age deviation in magnitude. The width or duration corre-
sponds to a number of sample points, N. For each sample
vi, when compared to vi-1cycle where the deviation in
magnitude is outside the maximum allowable deviation, a
counter is incremented. For each sample vi that is within
Figure 3.6 Addition of Impulsive Transient to the Fundamental Frequency Waveform
the maximum allowable deviation, the counter, if greater
than 0, is decremented. If the count reaches N, a trigger
occurs.
Once an event is detected, instantaneous waveform infor-
mation is recorded for all instrument channels. The fol-
lowing information is required to specify how much
information is recorded:
Before (Pre-trigger) Cycles
After (Post-trigger) Cycles
The Before and After items allow a variable number of
cycles before and after the disturbance to be recorded.
Setting these values to 0 causes one cycle of data to be
recorded for each event - the cycle in which the transient
was detected. Typical values for these settings are 1 and
2 cycles respectively, with a maximum of 7 and 15
respectively.
Note that RMS Variation events will often result in a
transient event being triggered and recorded as well.
Since the RMS Variation sub-system typically records
more waveform information than the transient sub-sys-
tem, the recorded transient record is not saved.
Figure 3.7 Waveshape Fault Detection
this Delta is what is measured
















































