Page 22
Ÿ
Quick Start
Have User
“Rex” bypass
PortServer
Command
Shell, connect
directly to
Host
“Corporate”
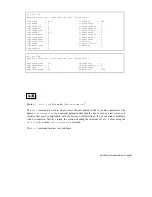
First, we create table entries for the host named “Corporate,”
including its IP address (152.83.151.1 is a “phony” name used
here for an example). Note that the “ip=” part is not necessary
if you have IP name service.
#>set host name=corporate ip=152.83.151.1
(You can inspect the Host table at any time by typing
set
host
with no other parameters.)
Next, we configure the PortServer software so that user “Rex”
is an auto user, automatically connected to a destination host
dest:
#>set users name=rex auto=on
#>set users name=rex dest=152.83.151.1
#>set users name=rex dport=23
(Again, 152.83.151.1 is a “phony” IP address; you would use
the real IP address for the host named “Corporate.”)
Setting
dport
is necessary to establish a terminal session with
the other host. The value 23 means a telnet-type terminal,
which will ask Rex to log in again at Corporate. An entry of
513 would specify Rlogin services, and Rex would auto-
matically be logged in as long as his login on “Corporate” is
the same user name. Check your operating system documen-
tation for service numbers.
set
commands are discussed in detail on page 38.