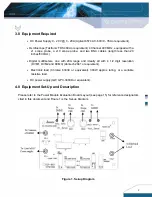
11
8.3 Dynamic Characteristics
8.3.1 Output Voltage Deviation
Output Voltage Deviation is defined as the response of the converter to a sudden step change
in the output load current. The output voltage deviation is characterized by two parameters:
Maximum Output Voltage Deviation and Response Time (please refer to the data sheet for the
detailed specification). The value of dynamic resistance for a defined step current is defined as:
Imax
Vout
R
dynamic
*
5
.
0
=
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Adjust the input voltage to the desired operating point.
3) Set the electronic or resistive load at 50% of maximum load.
4) Change channel 1 to scope probe and measure across the
.
dynamic
R
5) Set the switch SW1 to the “OFF” position to enable the converter.
6) Set channel 2 on the oscilloscope to be AC coupled and to 50mV/Div and for 50uS/Div. Set
the trigger to auto and adjust the trigger point at a negative going pulse for step load
change from 50% to 100% of Io or adjust the trigger point at positive going pulse for step
load change from 100% to 50% (Please refer to data sheet)
7) Measure the Peak deviation and capture the waveform as required.
8.3.2 Turn-On Transient Time
Turn-On Response Time is defined as the time it takes for the output to rise to within
90% of its
final value from the time when the converter is enabled. The rise time is deliberately made
slower to reduce the inrush current and to eliminate any overshoot in the output voltage. These
test functions have two categories.
1) Turn on the module by using the External switch to control input voltage.
2) Turn on module by using the Enable on/off.
Note:
There is a difference in performance in each mode - please refer to the data sheet for
the detailed specification.