CY4541 EZ-
PD™ CCG4 Evaluation Kit Guide, Doc. No. 002-10353 Rev. *E
48
Appendix A: Terminology
This guide assumes that the user of the CCG4 board is familiar with the fundamentals of Type-C connectivity and the USB Power
Delivery protocol. A brief description of Type-C terms is provided here for reference.
▪
Alternate Modes: A feature of a USB Type-C system where one or both of the SuperSpeed lanes may be repurposed for
use with a different serial protocol, such as a DisplayPort, eSATA, or Thunderbolt.
▪
Client: A USB peripheral such as a hub, docking station, or monitor.
▪
Configuration channel (CC): A USB Type-C bus wire used to transmit protocol signals. This is a half-duplex
300-kHz signal.
▪
Consumer: A Type-C port that sinks power from VBUS.
▪
DisplayPort: A digital display interface standard developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association. It is used
primarily to connect a video source to a display such as a computer monitor.
▪
Downstream facing port (DFP): A USB Type-C port on a host or a hub to which devices are connected and a default
power source.
▪
Dp, Dn: USB Type-C bus wires used to transmit and receive USB 2.0 data.
▪
Dual-role port: A USB Type-C port that can operate as either a DFP or a UFP, and either as power provider or power
consumer.
▪
Electronically Marked Cable Assembly (EMCA): A USB cable that includes an IC that reports cable characteristics (such
as current rating) to the Type-C ports.
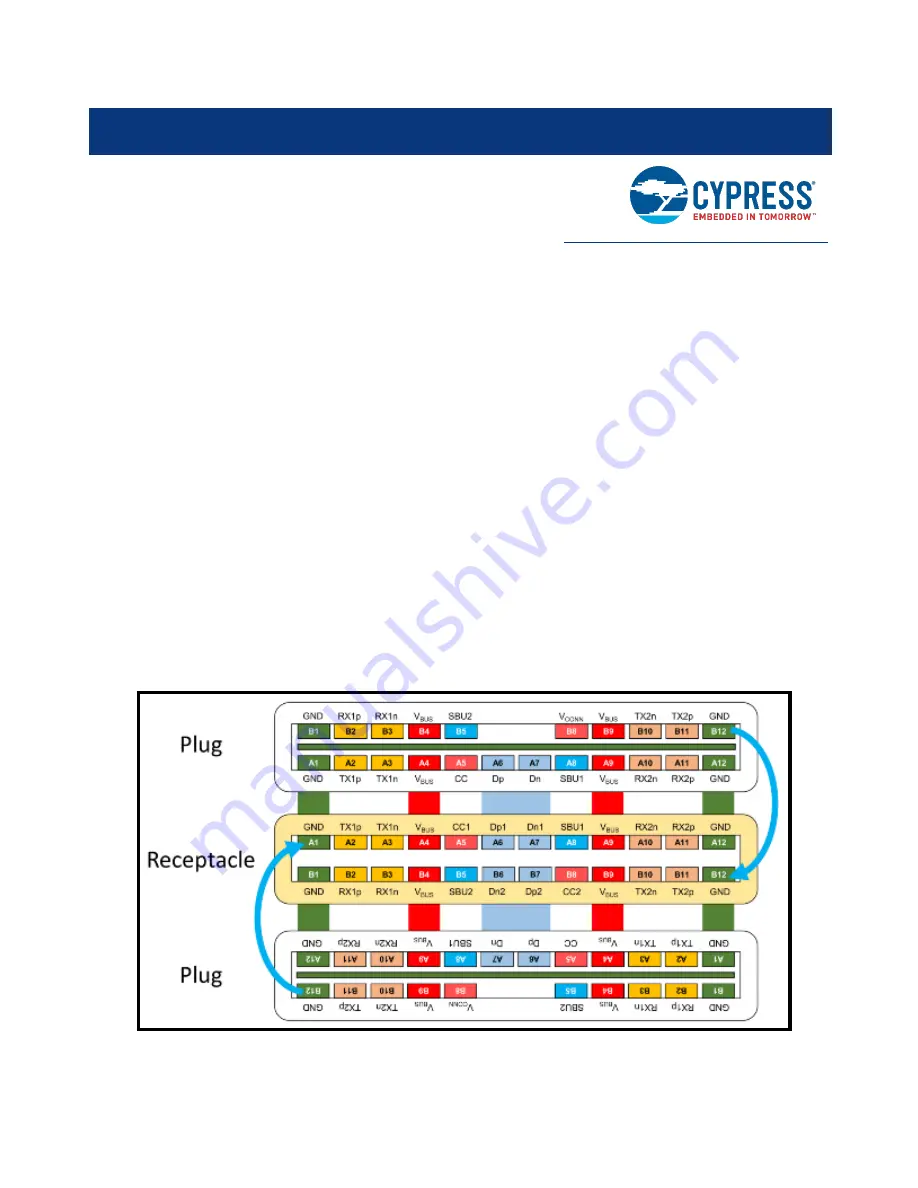
Figure 35: USB Type-C Plug and receptacle
















































