52
Commander SE Advanced User Guide
Issue Number: 4
0
Coast stop
1
Ramp stop
2
Ramp stop + timed DC injection braking
3
Injection braking stop with detection of zero speed
4
Timed injection braking stop
Stopping is in two distinct phases: decelerating to stop, and stopped.
Once modes 3 or 4 have begun the drive must go through the ready state before being restarted either by stopping, tripping
or being disabled.
See section 12.29
Stopping Modes
on page 194 for further information.
This parameter has 3 settings as follows:
0
Disabled
1
Stop
2
Ride through
In the disabled mode the drive is not looking for a mains loss and will continue to operate only as long as the DC Bus remains
within specification.
If either of the other two modes are selected the drive will decelerate on mains loss at the required rate to feed power back
from the motor onto the DC Bus to supply the drive control board. Mains loss is detected when the DC Bus falls below 430V
(225V on 200V product) after which the drive regulates the link voltage to 430V (225V on 200V product) with a proportional
controller changing the demanded current in the motor.
The current demand is fed to the frequency changing current controller and therefore the gain parameters
4.13
and
4.14
must
be set up for optimum control.
The difference between modes 1 and 2 is when the mains re-appears. In the stop mode the drive will continue to decelerate
until the machine stops, while in the ride through mode the machine will accelerate again to its normal running speed. In the
stop mode, the deceleration to stop, after mains has been re-applied will be according to the deceleration mode selected with
the ramp mode parameter (
2.04
).
When the drive goes into Mains Dip Ride through or Mains Stop Mode, the left hand display will show ‘AC’.
Mains dip time to stop
When the drive goes into a mains dip, the time taken for the motor to decelerate to stop will be dependant on the set
deceleration ramp and the inertia of the load. The drive will decelerate the load accordingly to keep the DC bus above the
voltage trip level. The time taken to decelerate the motor will always be equal to or less than the set deceleration ramp, it will
never be greater.
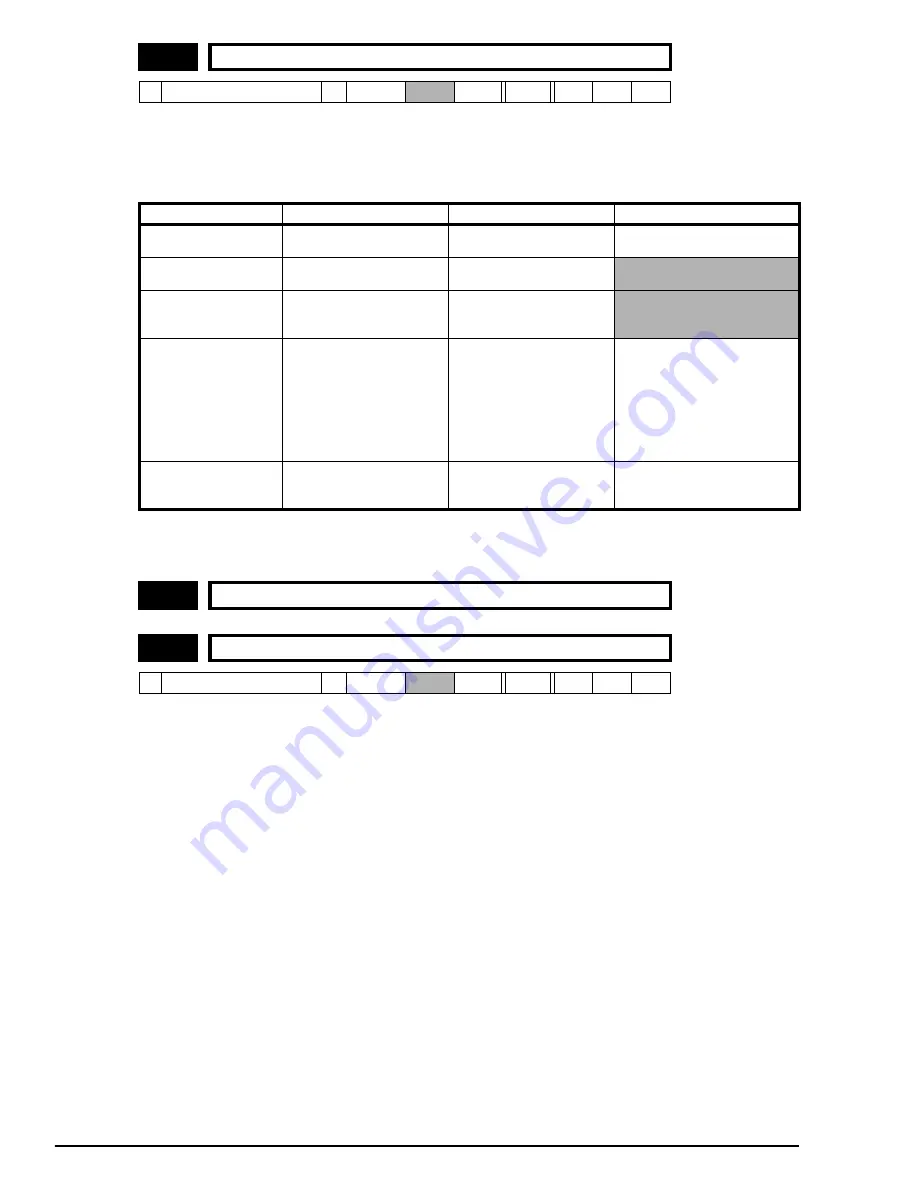
6.01
Stop mode selector
Ú
0 ~ 4
Ö
1
RW
Uni
Stopping Mode
Phase 1
Phase 2
Comments
0: Coast
Inverter disabled
Drive cannot be re-enabled
for 2s
Delay in phase 2 allows rotor flux
to decay.
1: Ramp
Ramp down to zero
frequency
Wait for 1s with inverter
enabled, then disable
2: Ramp + timed DC
injection braking
Ramp down to zero
frequency
Inject DC at level specified by
6.06
for time specified by
6.07
3: DC with zero speed
detection
Low frequency current
injection at the level
programmed in
6.06
with
detection of low speed before
next phase.
Inject DC at level specified by
6.06
for time specified by
6.07
The drive automatically senses
low speed and therefore it
adjusts the injection time to suit
the application. If the injection
current level is too small the
drive will not sense low speed
(normally a minimum of 50-60%
is required).
4: Timed injection
braking stop
Inject DC at level specified by
6.06
for time specified by
6.07
-1s.
Inject DC at level specified by
6.06
for 1s
The minimum total injection time
is 1s for phase 1 and 1s for
phase 2, i.e. 2s in total.
6.02
Unused parameter
6.03
AC supply loss mode selector
Ú
0 ~ 2
Ö
0
RW
Uni
















































