WM8940
Rev 4.4
11
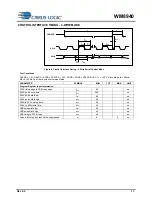
TERMINOLOGY
1.
Full-scale input and output levels scale in relation to AVDD or SPKVDD depending upon the input or output used. For
example, when AVDD = 3.3V, 0dBFS = 1V
rms
(0dBV). When AVDD < 3.3V the absolute level of 0dBFS will decrease with a
linear relationship to AVDD.
2.
Input level to RIP and LIP in differential configurations is limited to a maximum of -3dB or performance will be reduced.
3.
Signal-to-noise ratio (dB)
– SNR is the difference in level between a reference full scale output signal and the device output
with no signal applied. This ratio is also called idle channel noise. (No Auto-zero or Automute function is employed in achieving
these results).
4.
Total Harmonic Distortion (dB)
– THD is the difference in level between a reference output signal and the first seven harmonics
of that signal. The reference output signal need not be at full scale amplitude; THD is typically measured using an output
power of 20mW into a 16ohm load, corresponding to a reference signal level of -5dB. However the stated test conditions
include input signal level, signal gain settings, output load characteristics and power supply voltages To calculate the ratio, the
fundamental frequency of the output signal is notched out and an RMS value of the next seven harmonics is calculated.
5.
Total Harmonic Distortion plus Noise (dB)
– THD+N is the difference in level between a reference output signal and the sum of
the harmonics, wide-band noise and interference on the output signal. To calculate the ratio, the fundamental frequency of the
output signal is notched out and an RMS value of the total harmonics, wide-band noise and interference is calculated.
6.
Channel Separation (dB)
– Also known as Cross-Talk. This is a measure of the amount one channel is isolated from the other.
Normally measured by sending a full scale signal down