Page 7
4.4 Hardware Trigger
The microDAQ features a hardware trigger to enable the user to synchronise multiple microDAQ’s
and to calculate the timing of the measurements made. The hardware trigger takes the form of a
pulse train. Each time the microDAQ receives a positive edge, it will generate a set of
measurements for all the channels configured in the system.
4.4.1 Hardware Trigger Input.
The hardware trigger input is a 5V TTL square wave pulse train. Minimum frequency 2Hz and
maximum frequency 1.2KHz (32 channel scanner, real world application – theoretical maximum is
determined by the number of channels on the scanner. 64 channel units streaming data via TCP
comms will struggle to stream faster than around 600Hz)
4.4.2 Timing Information
The hardware trigger allows the user to calculate the time of each measurement. For example if the
hardware trigger were running at 100Hz then the user would receive 100 measurements per
channel per second. The first pulse would generate the first set of measurements and 10ms later
the second pulse would generate the second set and so on. When the hardware trigger is
activated, the microDAQ will wait for the first pulse. The time that this first pulse is generated can be
measured by the user and therefore the time of the first set of data and all subsequent sets can be
determined. For more details on hardware trigger timing a technical paper is available – Chell
document no. 900118 (this paper was developed for the CANdaq but applies to the microDAQ as
well).
4.4.3 Software Control
The hardware trigger mode is activated by the T command over the CAN or Ethernet interfaces.
The T command can be used to enable the hardware trigger that will cause the microDAQ to stop
free-running and wait for the first pulse. The disable command will return the microDAQ to free-
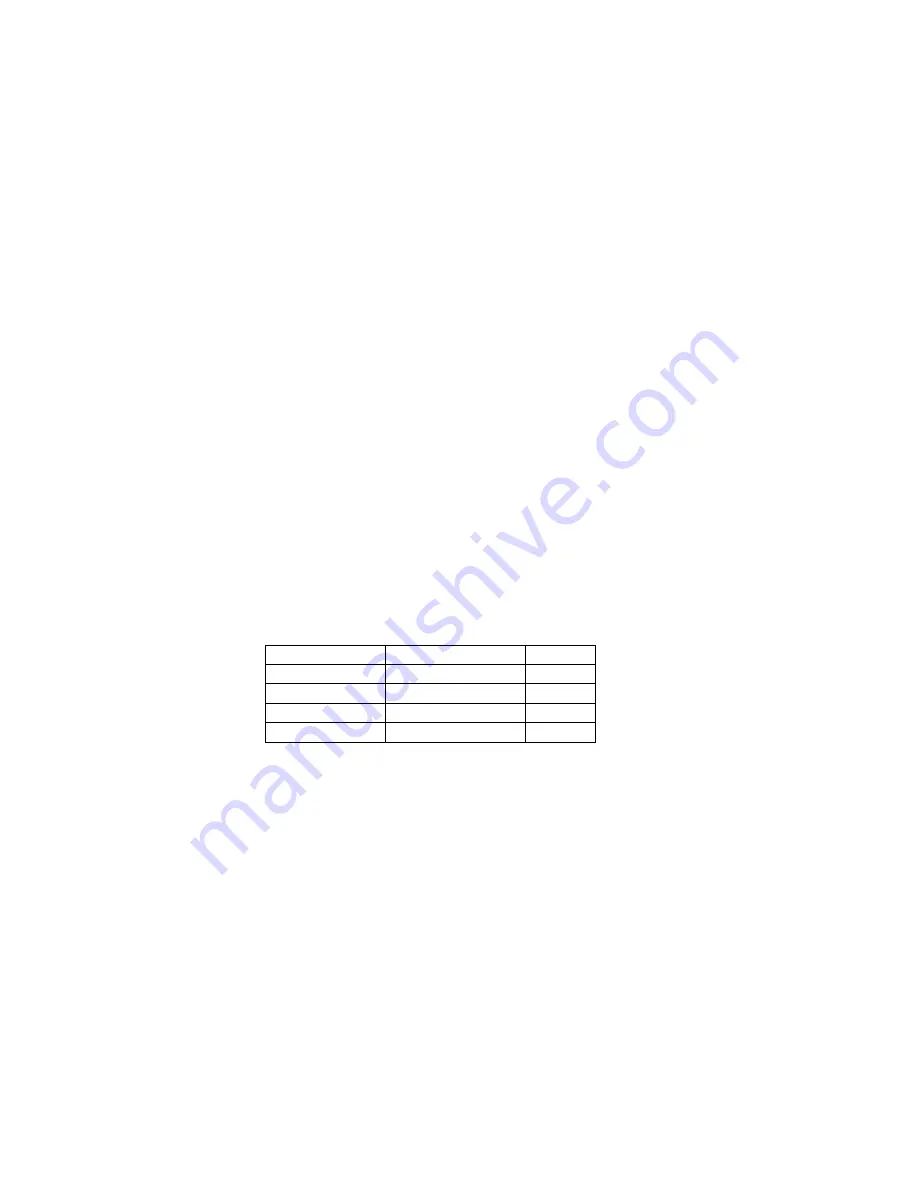
running. The command structure is as follows:
Command
Interface
On / Off
T01
CAN
Off
T11
CAN
On
T02
Ethernet
Off
T12
Ethernet
On
The hardware trigger can also be set to auto enable on power up which means that the microDAQ
will not go into free-running mode after initialisation and will instead wait for the first hardware
trigger pulse. In this instance the blue LED will not flash at a constant rate after initialisation and will
actually turn off. This feature can be enabled/disabled from the embedded webserver
configuration.








































