Page 104
-1
0
1
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Seconds
4 (Hz)
1 (Hz)
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)
The French mathematical physicist Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier found that it
was possible to represent any waveform in the time domain as a sum of infinitely
many sine and cosine terms.
FFT analysis can be performed on certain sound meter instrumentation and is
where the instrument takes the time varying input signal and displays the
calculated frequency spectrum. The frequency spectrum can then be examined
to determine exactly which frequencies are causes for concern regarding noise
levels or for preventative maintenance.
Feedback
A very simplified public address system will consist of a microphone an amplifier
and a speaker. If sound from the speaker is detected on the microphone then
this sound will be amplified again and output to the speakers. If the gain of this
amplification is greater than one then the system becomes unstable and a high
pitch squealing noise is heard.
Frequency (Hz)
The number of cycles per unit of time measured in cycles per second (cps) and
associated with the unit symbol Hz (Hertz) after the German physicist Heinrich
Hertz.
1 cps = 1 Hz
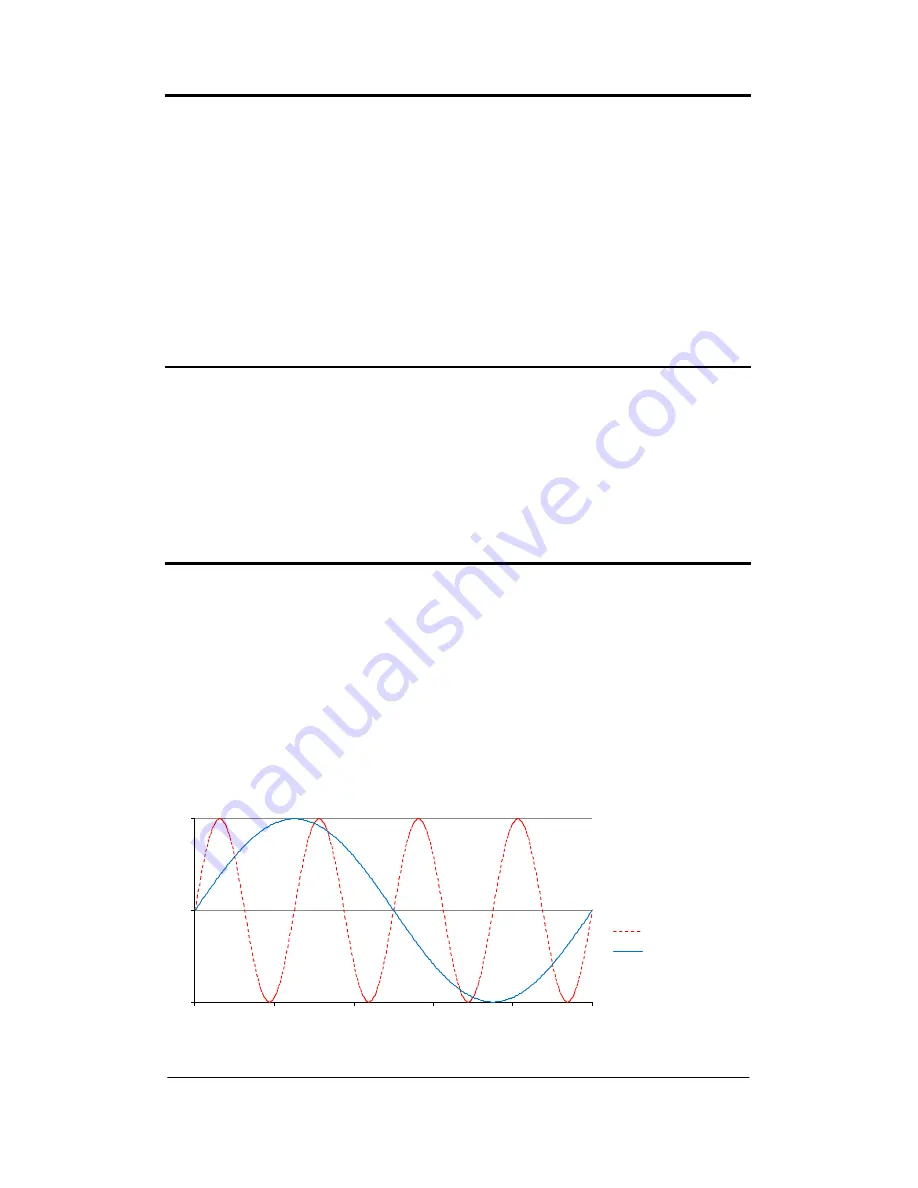
The graph below shows the solid line having one complete cycle in one second
and therefore having a frequency of 1Hz whereas the dotted line has four
complete cycles in one second and therefore has a frequency of 4Hz.
Frequency is universally given the descriptor f, therefore the graph below shows
f = 1Hz and f = 4Hz.
















































