145
9-2 Analyzing a Function Graph
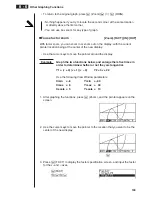
The following two graphs are used for all of the examples in this section, except
for the example for determining the points of intersection for two graphs.
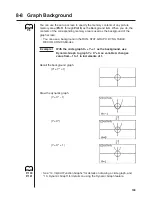
Memory location Y1 =
x
+ 1 Y2 =
x
(
x
+ 2)
(
x
– 2)
Use the View Window to specify the following parameters.
(A)
Xmin
= –5
Ymin
= –5
(B)
Xmin
= –6.3
Ymin
= –3.1
Xmax =
5
Ymax =
5
Xmax =
6.3
Ymax =
3.1
Xscale =
1
Yscale =
1
Xscale =
1
Yscale =
1
k
k
k
k
k
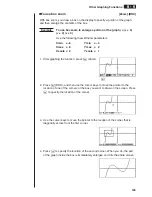
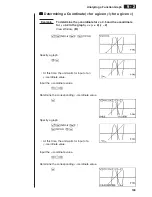
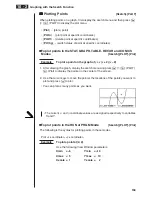
Determining Roots
Example
To determine the roots for
y
=
x
(
x
+ 2)(
x
– 2)
View Window:
(B)
!5
(G-Solv)
1
(ROOT)
(This puts the unit into standby waiting
for selection of a graph.)
• A “
k
” cursor appears on the graph that has the lowest memory area number.
Specify the graph you want to use.
c
• Use
f
and
c
to move the cursor to the
graph whose roots you want to find.
Determine the root.
w
• Roots are found starting from the left.
Summary of Contents for CFX-9970G
Page 22: ... CFX 9970G ...
Page 452: ...435 1 2 3 4 5 Program for Circle and Tangents No 4 Step Key Operation Display ...
Page 453: ...436 Program for Circle and Tangents No 4 Step Key Operation Display 6 7 8 9 10 ...
Page 454: ...437 11 12 13 14 15 Program for Circle and Tangents No 4 Step Key Operation Display ...
Page 455: ...438 16 17 18 Program for Circle and Tangents No 4 Step Key Operation Display ...
Page 458: ...441 1 2 3 4 5 Program for Rotating a Figure No 5 Step Key Operation Display ...