CDE360 Vector Control AC Drive Chapter 6 Parameters Description
Multi-pump control mode 4:
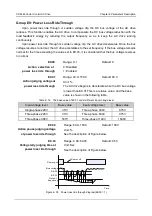
Pump adding logic
The same with mode 3.
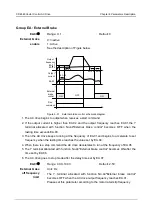
Pump removing logic
The same with mode 3.
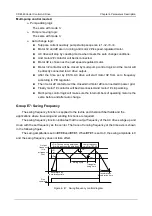
Auto change logic
Suppose current auxiliary pump startup sequence is 1->2->3->4.
Motor 1# and 2# are in running,and motor 2# is speed-regulated motor.
AC drive will stop by coasting mode when meets the auto change conditions.
And motor 2# contactor will be disconnected.
Motor 3# is chosen as the next speed-regulated motor.
Motor 3# contactor will be closed by multi-pump control logic.And the motor will
be directly connected to AC drive output.
After the time set by E6.18,AC drive will start motor 3# from zero frequency
according to PID regulator.
Then motor 2# contactor will be closed.And motor 2# is connected to power grid.
Finally motor 1# contactor will be disconnected.And motor 1# stop working.
Multi-pump control logic will make sure the total numbers of operating motor is the
same before and after auto change.
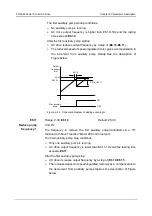
Group E7: Swing Frequency
The swing frequency function is applied to the textile and chemical fiber fields and the
applications where traversing and winding functions are required.
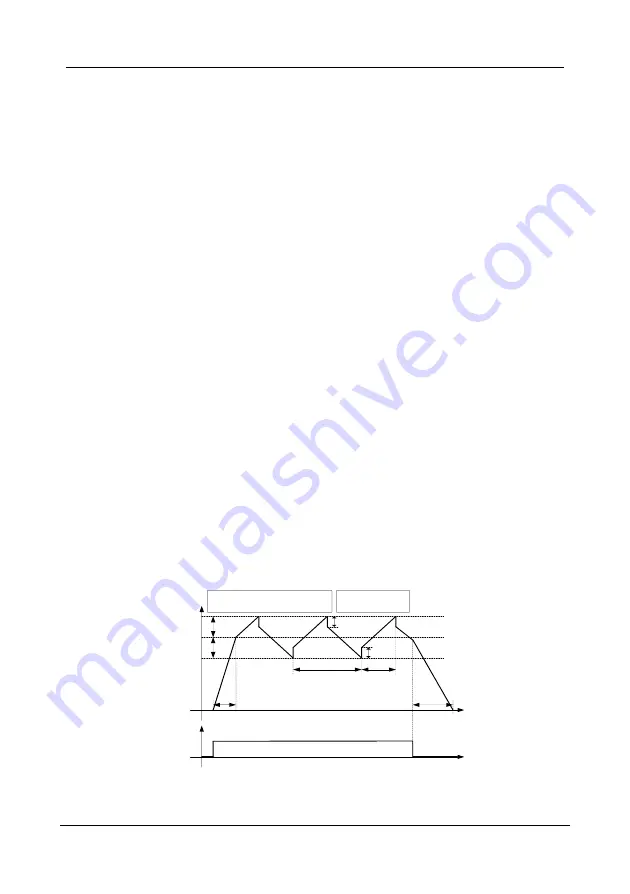
The swing frequency function indicates that the output frequency of the AC drive swings up and
down with the set frequency as the center. The trace of running frequency at the time axis is shown
in the following figure.
The swing amplitude is set in
E7.00
and
E7.01
. When
E7.01
is set to 0, the swing amplitude is 0
and the swing frequency does not take effect.
Accelerate by
acceleration time
Run
command
+Dw Positive swing amplitude
-Dw Negative swing amplitude
+D
w
-Dw
Jump frequency
Jw = Dw * E7.02
Jw
Jw
Decelerate by
deceleration time
Swing cycle
Triangular
rising time
Set frequency
Fset
Output
frequency
(Hz)
Figure 6- 47 Swing frequency control diagram