To determine DFT, induce VF (or PVT or ventricular
fl
utter if VF is not inducible). Attempt to convert the
arrhythmia with a 31-J shock; if conversion is successful, then induce again and attempt to convert the
arrhythmia at 29 J. Continue in this manner, decreasing the energy level until failure to convert VF occurs or 3 J
is successful. If the initial conversion at 31 J is unsuccessful, reposition the lead, or reverse polarity, or add an
additional lead. The energy level that last successfully converted the arrhythmia is the DFT. It is a matter of
clinical judgment as to what constitutes a demonstration of reliable conversion.
Shocks intended for VF therapy should be programmed with a 10 J safety margin above the shock energy
level that the physician determines is required for successful VF conversion. In some situations an alternative
safety margin may be determined by the physician to be adequate above the shock energy level required
for successful VF conversion.
NOTE:
Since the results of any single test may be an example of statistical variation, a one-time conversion of
a rhythm disturbance at a particular energy level does not guarantee or assure that the energy level is reliable
for conversion. As a safety margin, it is recommended that you perform the conversion test at the DFT two
times if the DFT is 31 J, or one time if the DFT is 29 J with no failures to convert.
Step J: Implant the Pulse Generator
1.
Program the Tachy Mode to Off.
2.
Verify magnet function and wanded telemetry to ensure the pulse generator is within acceptable range
to initiate interrogation.
3.
Ensure that the pulse generator has good contact with surrounding tissue of the implantation pocket, and
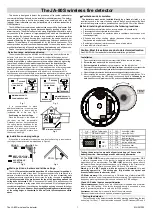
then suture it in place to minimize device migration (for suture hole location illustrations, refer to "Lead
Connections" on page 44). Gently coil excess lead and place adjacent to the pulse generator. Flush
the pocket with saline solution, if necessary, to avoid a dry pocket.
WARNING:
Do not kink, twist, or braid the lead with other leads as doing so could cause lead insulation
abrasion damage or conductor damage.
64