OMD10078 rev F
8
1.1.1 Operation with ONE charging level
This type of charge is generally used with sealed lead acid batteries that, owing to
the manufacturing technology, have a very narrow voltage range. In fact, the nominal
charging voltage ranges between 2.25÷2.27 V/cell, with a maximum value of 2.3 V/cell.
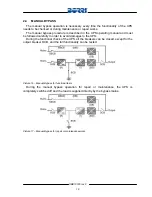
The picture below shows the charging curves at different charging currents; the
higher is the current, the higher is the restored capacity versus time, the lower is the
recharging time.
Picture 3 – Operation with ONE charging level
1.2
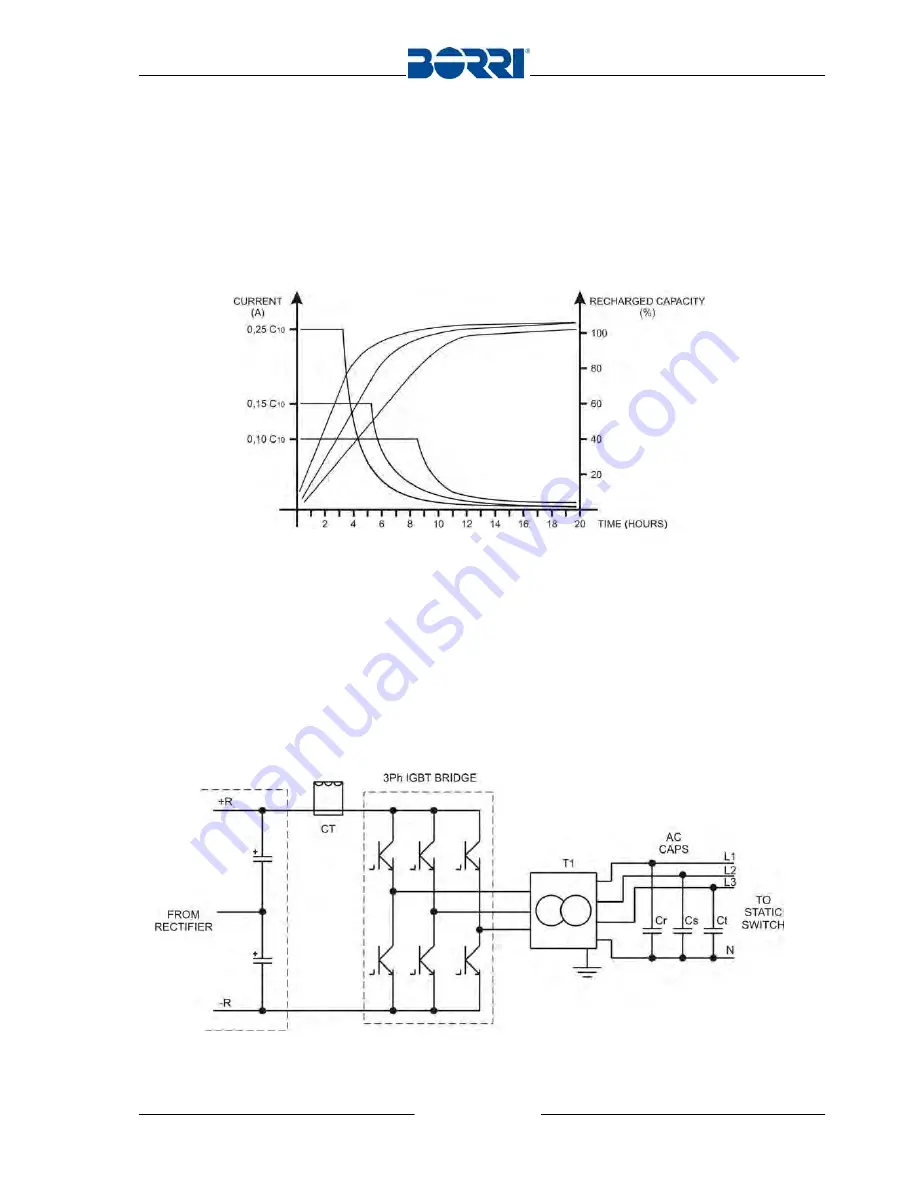
INVERTER
The inverter converts the DC input voltage to AC voltage, stabilized in frequency and
RMS value.
The DC voltage is converted by the IGBT bridge, that uses six switches, controlled
using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) technology at high commutation frequency. The
PWM generation as well as the control of the operating variables is completely
managed by the microprocessor.
The current transducer CT provides for the monitoring of the input current. Its
feedback signal is managed by the microprocessor to activate the current limitation (see
2.2.3) and the IGBT protection (see 2.2.4).
Picture 4 – Inverter
The output transformer provides galvanic insulation between DC and AC side, as
well as voltage adaptation. Its integrated inductance forms, together with the AC