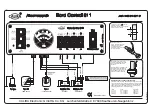
I01�High-voltage�Components
12.�Technical�Safety�Precautions
173
Index
Explanation
1
High-voltage�safety�connector�("Service-Disconnect")
2
Fuse�block,�front
3
Safety�battery�terminal�(SBK)
4
12 V�battery
5
Intelligent�battery�sensor�(IBS)
6
Crash�Safety�Module�(ACSM)
7
High-voltage�battery�unit
8
Battery�management�electronics�(SME)
9
Signal�generator�for�test�signal�of�the�high-voltage�interlock�loop�in�the�battery
management�electronics
10
Evaluation�circuit�for�test�signal�of�the�high-voltage�interlock�loop�in�the�battery
management�electronics
11
Cells�of�the�high-voltage�battery
12
Switch�contactor,�fuse�and�series�resistor�in�the�high-voltage�battery
13
Convenience�charging�electronics�(KLE)
14
Range�extender�electrical�machine
15
Range�Extender�Electrical�Machine�Electronics�(REME)
16
Evaluation�circuit�for�test�signal�of�the�high-voltage�interlock�loop�in�the
electrical�machine�electronics
17
Electrical�machine�electronics�(EME)
12.2.�Starting�and�shutting�down�the�high-voltage�system
The�master�control�unit�for�the�control�of�the�high-voltage�system�is�the�electrical�machine�electronics.
12.2.1.�Starting
The�sequence�for�starting�the�high-voltage�system�is�always�the�same�irrespective�of�which�of�the
following�events�was�the�trigger:
•
Terminal�15�is�switched�on�or�driving�readiness�is�established
•
Charging�the�high-voltage�battery�should�start
•
"Preparation"�of�the�vehicle�for�the�journey�(climate�control�of�the�high-voltage�battery�or�the
passenger�compartment).
The�individual�steps�for�starting�the�high-voltage�system�are:
1
EME�control�unit�requests�starting�via�bus�signal�at�the�PT-CAN�and�PT-CAN2
2
The�high-voltage�electrical�system�is�checked�using�self-diagnosis�functions