2
1
History
The Leeb measuring method was first brought into measurement technology in 1978. It is defined as the
quotient of an impact body’s rebound velocity over its impact velocity, multiplied by 1000. Harder materials
produce a higher rebound velocity than softer materials. For a specific group of material (e.g. steel,
aluminum. etc.), Leeb hardness value represents a direct relationship to its hardness properties. For ordinary
metal, conversion curves of hardness HL versus other standard static hardness (HB, HV, HRC, etc.) are
available, enabling you to convert HL into other hardness values.
Leeb Hardness Test (definition)
An impact body with a spherical test tip made of tungsten carbide is propelled against the sample surface by
a spring force and then rebounds back. At a distance of 1mm from the sample surface, the impact and
rebound velocity of the impact body are measured by the following method: A permanent magnet embedded
in the impact body, when passing through the coil in its coil holder, induces in the coil an electric voltage
proportional to the velocities of the magnet. Leeb hardness is expressed by the following formula:
HL=1000
×
(V
B
/V
A
)
Where: HL is Leeb Hardness
V
B
is the rebound velocity of the impact body
V
A
is the impact velocity of the impact body
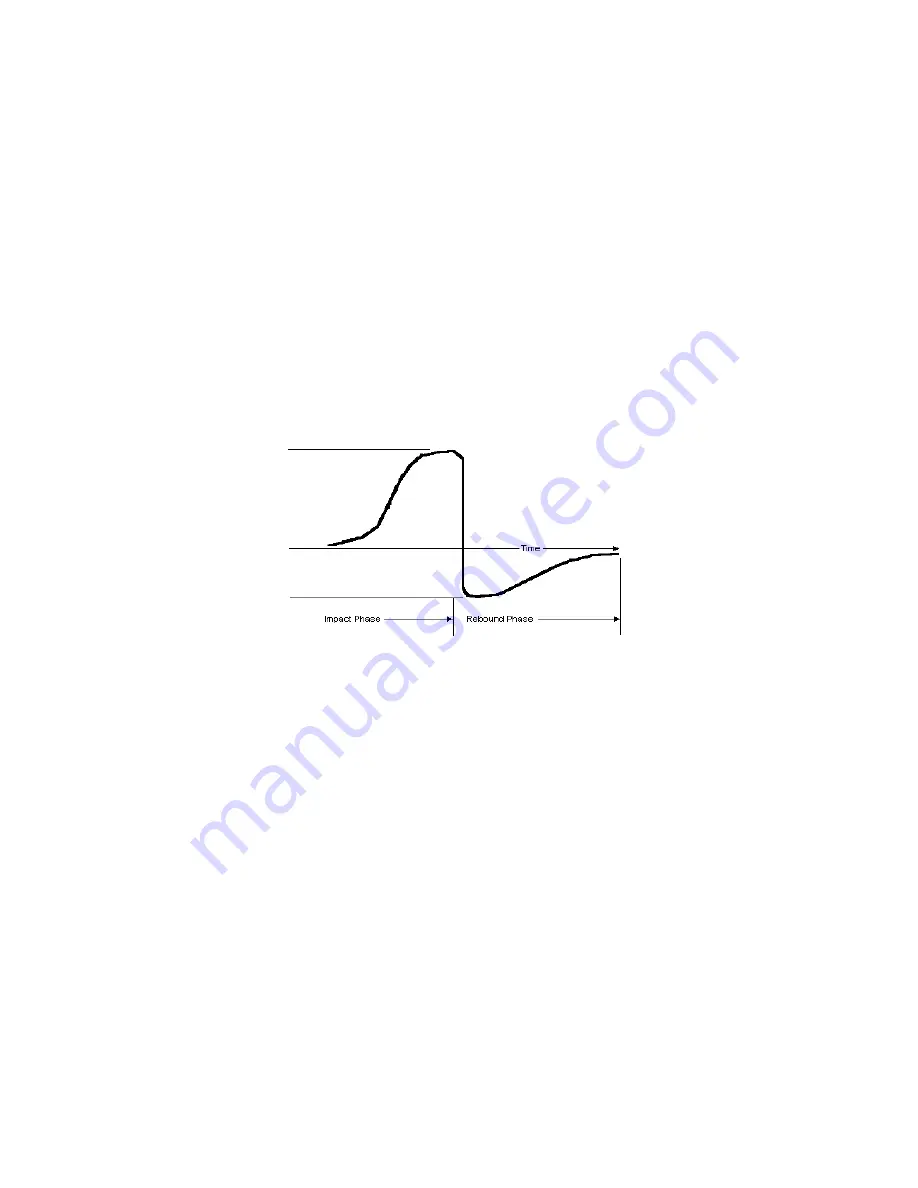
The voltage characteristic of output signal, when the impact body passes through the induction coil is
illustrated in the following figure:
Voltage characteristic of output signal
A Leeb’s Hardness Tester measures the hardness of sample material in terms of Hardness Leeb (HL), which
can be converted into other Hardness units (Rockwell B and C, Vicker, Brinell and Shore D).
Notation of Leeb Hardness
When measuring the hardness of a sample material using the traditional static hardness testing method, a
change of applied pressure will result in a change in the hardness reading.
For example: 720HLD
≠
720HLC
Because different converting curves are obtained from different impact devices, when converting hardness L
into another hardness value the notation for the converted hardness value should include the impact device
used.
2
Features and Applications
Specifications
Display: LCD
Accuracy: +/-3HL at HL=800 (0.4%)
Measuring range: 170-960HL
Conversion: HL-HRC-HRB-HB-HV-HS-HRA-σb
Materials: 9 different common materials
Memory: 99 data can be stored and re-readable
Impact device: D
Power on/off: Auto
Power supply: DC 9V Ni-MH rechargeable battery





























