16
10
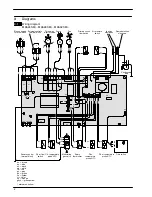
Electronic control/ignition p.c.b.
10.1
Function
From other boiler devices....
C.h. temperature probe NTC
D.h.w. temperature probe NTC
D.h.w. flow switch
Primary circuit flow switch
Air pressure switch
Flue temperature probe NTC
Safety thermostat
Flame detection electrode
Room thermostat (if fitted)
Time switch
On
the
Electronic
control/ignition
p.c.b.......
Function control
C.h. temperature adjustment
D.h.w. temperature adjustment
Boiler reset button
(control panel fascia)
Inlet Information
Pump
Three way diverter valve
On---off operators (gas valve)
Modulation operator (gas valve)
Fan
Ignition electrodes
Appliance operation lights*
Lock---out signal lamp*
*control panel fascia
Outlet command
Fig. 28
The fundamental function of the Electronic control/igni-
tion p.c.b. is that of controlling the boiler in relation to
the external needs (i.e. heating the dwelling or heating
the water for d.h.w. use) and operating in order to keep
the temperature of the hydraulic circuits constant.
This is obviously possible within the useful power and
maximum working temperature limits foreseen.
Generally, the Electronic control/ignition p.c.b. receives
inlet information coming from the boiler (the sensors)
or from the outside (knobs, room thermostat, etc.), pro-
cesses it and consequently acts with outlet commands
on other components of the boiler (Fig. 28).
The Electronic control/ignition p.c.b. is also a full se-
quence ignition device and does a sequence of oper-
ations (ignition cycle) which lead to the ignition of the
gas at the burner
It checks the presence of the flame during the entire
period in which it is activated, supplies the fan and
checks its functioning by means of the signal coming
from the air pressure switch.
The Electronic control/ignition p.c.b. has a
safety func-
tion
and any incorrect interventions or tampering can
result in conditions of dangerous functioning of the
boiler.
The Electronic control/ignition p.c.b. can lock the func-
tioning of the boiler (lock state) and stop its functioning
up to the resetting intervention. The lock is signalled by
the lighting of the lock---out signal lamp and the device
can be reset only by using the boiler reset button
placed on the control panel fascia.
Some components which are connected to the device
can activate the lock state. The causes of a lock state
could be:
f
The intervention of the safety thermostat (over-
heat of the primary circuit).
f
The intervention of the flue temperature probe
(overheat of the combustion products).
f
A fault on gas supply.
f
Faulty ignition (faulty ignition electrodes, their wir-
ing or connection).
f
Faulty flame detection (faulty detection electrode,
its wiring or connection).
f
Faulty condensate drainage.
f
Gas injectors blocked.
f
Faulty modulation gas valve (faulty on---off oper-
ators or not electrically supplied).
f
Faulty Electronic control/ignition p.c.b..
Other components like the air pressure switch can tem-
porarily stop the ignition of the burner but allow its igni-
tion when the cause of the intervention has stopped.
Fig. 52 shows the sequence of the operations that are
carried out at the start of every ignition cycle and during
normal functioning.
10.2
Selection and adjustment devices
On the Electronic control/ignition p.c.b. several selec-
tion, adjustment and protection devices are located.
(Fig. 29).