Cooling Oil -
Anytime the pump is
removed from operation, the cooling
oil in the motor ousing should be
h
checked visually for oil level and
contamination. To check oil, set unit
upright. Remove cap screws (6), lift
conduit box assembly (4) from motor
housing (3),
disconnect
Do Not
wiring from motor leads. With a
flashlight, visually inspect the oil in
the motor housing (3) to make sure it
is clean and clear, light amber in color
and free from suspended particles.
Milky white oil indicates the presence
of water. Oil level should be just
above the motor when pump is in
vertical position.
Seal Chamber -
Drain oil from seal
chamber by placing pump on its
side with pipe plug (18) downward
and remove pipe plug (18). If the oil
is found to contain c
onsiderable
water or other
contamination, the
shaft seal (19) should be inspected
and replaced if required.
After leak is repaired, dispose of old
oil properly, and re ill with new oil.
f
Use soap solution around the sealed
areas above the oil level and nspect
i
joints for "air bubbles". If, after ive
f
minutes, the pressure is still holding
constant, and no "bubbles" /oil
seepage is observed, slowly bleed the
pressure and remove the gauge
assembly. Replace oil. Leek must be
located and repaired if pressure does
not hold.
Seal Chamber -
Check that seal
c
hamber is full of oil by removing
pipe plug (18). Apply pipe sealant to
p
ressure gauge assembly and tighten
into hole in bearing housing (16).
P
ressurize seal chamber to 20-25 PSI
and check for leaks.
Oil Replacement
- Set unit upright
and re ill with new cooling oil as per
f
table. Fill to just above motor as an air
space must remain in the top of the
housing to compensate for oil
expansion. Reassemble the o-ring (5)
and conduit box (4) to motor housing
(3). Apply thread locking compound
to cap screws (6) and place into holes
and torque to 15 ft/lbs.
Oil Replacement:
Seal Chamber -
Refill chamber
c
ompletely full with new cooling oil
or reuse the uncontaminated oil.
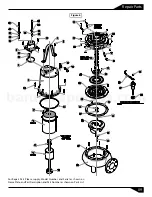
Figure 2
a) Inspect motor chamber for oil level
and contamination.
b) Inspect impeller and body for
excessive build-up or clogging.
c) Inspect motor, bearings and shaft
seal for wear or leakage.
NOTE: Item numbers in ( ) refer to
Figure 6.
Servicing
Ÿ
If oil is found to be clean and
uncontaminated
(measuring
above 15 V breakdown), re ill the
k
f
housing.
Ÿ
If oil is found to be dirty or
contaminated (or measures below
15 breakdown), the pump must
kV
be carefully inspected for leaks at
the shaft seal, conduit box, o-rings,
pipe plug and pressure valve,
before re illing with oil. To locate
f
the leak, perform a pressure test.
Oil Testing
Ÿ
Drain oil into a clean, dry container
p
lacing pump on it’s side, remove
cap crews (6), lift conduit box
s
assembly (4) from motor housing
(3). In sepa ate container drain seal
r
chamber by removing pipe plug
(18).
Ÿ
Check oil for contamination using
an oil tester with a range to 30
kV
breakdown.
Pressure builds up extremely
fast, increase pressure by
"TAPPING" air nozzle. Too
much pressure will damage
seal.
DO NOT exceed 10 PSI
in housing and 20-25 PSI in
seal chamber.
Pressure Test
Motor Housing -
Oil should be at
normal level. Remove pressure valve
(10) from motor housing (3). Apply
pipe sealant to pressure gauge
assembly and tighten into hole (See
Figure 2). Pressurize motor housing to
10 PSI.
DO
NOT
overfill
oil.
Overfilling of housing with oil
can create excessive and
dangerous hydraulic pressure
which can destroy the pump
and create a hazard.
Overfilling oil voids warranty.
05
Service
Cooling Oil
Recommended Supplier/Grade
BP
Enerpar SE100
Conoco
Pale Parafin 22
Mobile
D.T.E. Oil Light
Shell Canada
Transformer-10
Texaco
Diala-Oil-AX
barmesapumps.com