Page 14
IronHorse GSDA-CM-8 User Manual – 1st Ed. Rev. A – 10/15/19
RS-232 and RS-422/485 Connections to the RJ45 Modular Jack
The GSDA-CM-8 RS-232 and RS-422/RS-485 port uses a standard 8-pin RJ45 modular connector. A
standard 4- or 6-pin RJ11 or RJ12 modular connector may also be used as an alternative when making
RS-422/485 connections. When using RJ11 or RJ12 cable you are only connecting to the middle 4 or 6
pins of the RJ45 Modular Jack. A 4-pin modular connector uses the middle 4 pins, numbers 3 through
6 and the 6-pin modular connector uses the middle 6 pins, numbers 2 through 7. The use of an 8-pin
RJ45 modular connector will be required when making connections for RS-232.
There is currently NO standard wiring format for a RJ45 Modular connector when used in RS-232
or RS-422/485 applications. We have chosen to allow the use of a standard 4-, 6-, or 8-pin modular
connector in our wiring scheme. The RJ45 Modular Jacks pinout for the GSDA-CM-8 is as follows:
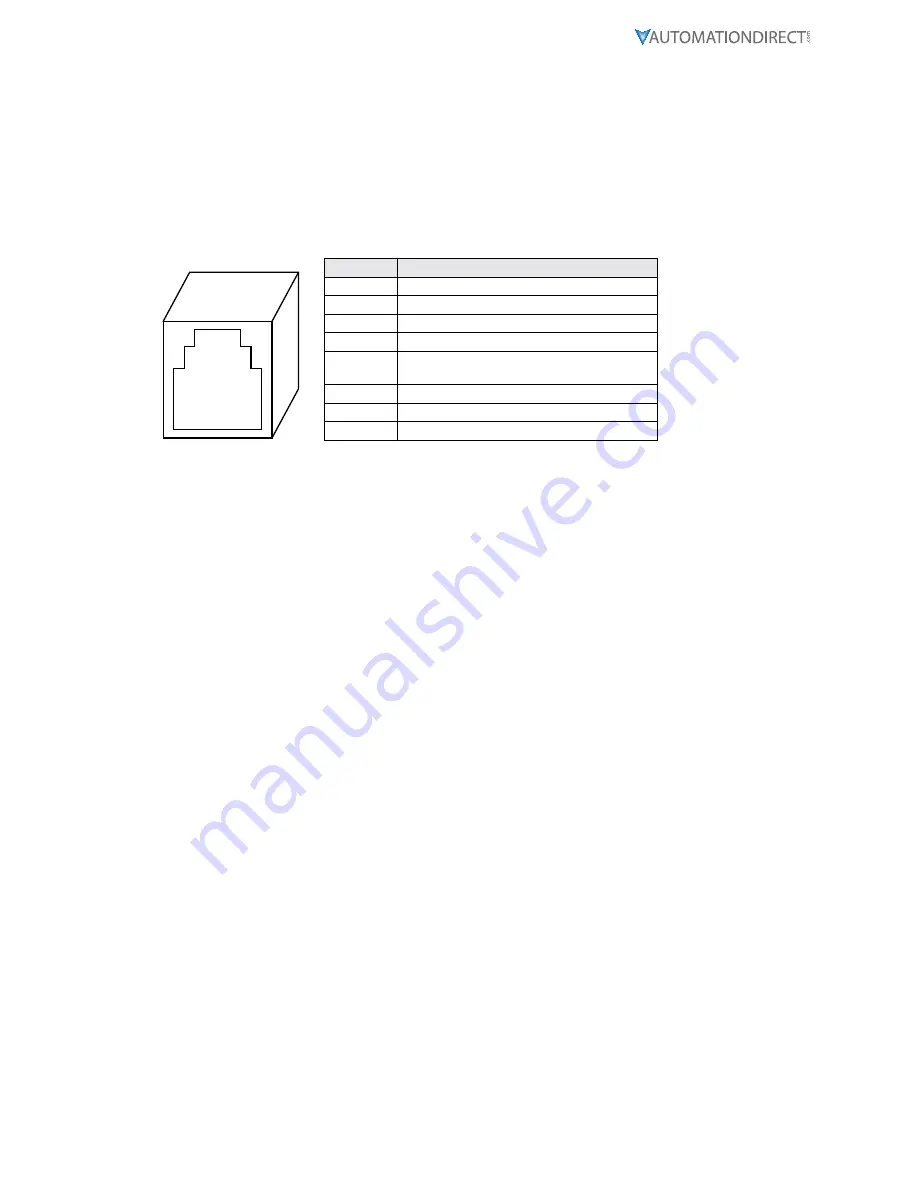
RJ45 Jack
Front
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
RJ45 Pin
Signal Description
1
RS232 Rx (Receive data)
2
No Connect
3
TxD+, RxD+ (+transmit/receive data line)
4
TxD-, RxD- (-transmit/receive data line)
5
Frequency generator out (Do not use for
RS232 communications)
6
Circuit Common, Signal Ground
7
Analog Input (0 to 5 VDC)
8
RS232 Tx (Transmit data)
There are minor differences between RS-232 and RS-422/485. RS-232 is a point-to-point interface
standard which is intended to allow two—and only two—devices to be attached to one another.
RS-422 and RS-485 are multi-point interface standards supporting one master and as many as 32
devices on the same lines or bus. Another key difference is that RS-422 and RS-485 are considerably
more tolerant to noisy environments. It is typically not recommended that RS-232 be run more than
50 feet. Specialty converters can be purchased to allow an RS-232 device to interface with one or
more units on a shared multi-point bus. Once the desired interface standard has been selected,
jumper JP1 should be positioned accordingly. Failing to do so will not damage the drive, but will
result in a lack of communication.
When connecting a device with an RS-422 or RS-485 port to an GSDA-CM-8 unit, connect the
multi-point bus in half-duplex mode. In this mode the T and are connected to the
unit’s RJ45 pin 3. The Transmit- and Receive- are connected to the unit’s RJ45 pin 4. It may also be
necessary to connect the unit’s Signal Ground, RJ45 pin 6, to the remote device’s Signal Ground. In
this configuration, the RJ45 pins 1 and 8 should remain disconnected.
When connecting a computer with an RS-232 port to an GSDA-CM-8 unit, not all of the available wires
have to be used. If a port with a DB-9 (9 pins) connector is used, then make the following connections:
•
DB9 pin 2 to RJ45 pin 8
•
DB9 pin 3 to RJ45 pin 1
•
DB9 pin 5 to RJ45 pin 6.
If a port with a DB-25 (25 pins) connector is used, then make the following connections:
•
DB25 pin 2 to RJ45 pin 1
•
DB25 pin 3 to RJ45 pin 8
•
DB25 pin 7 to RJ45 pin 6
In this configuration, the RJ45 pins 3 and 4 should remain disconnected.
Communications Troubleshooting
If communications with a computer aren’t working, there are a few things to check. First, make sure
the terminal program is communicating with the correct port (ie: COM1, COM2, etc.). This can be
difficult because the port numbers are not labeled on the back of most machines. Use the following
outline when troubleshooting new connections:
1)
Set the terminal program to 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, and half duplex.
2)
Set the terminal program to the selected serial port: COM1, COM2, etc. (guess if unknown)
3)
If necessary, unplug the cable from the selected serial port on the back of the computer.















































