Administrator’s Handbook
42
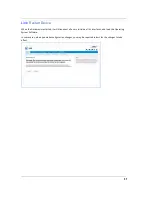
The
Wi-Fi Operation
function is automatically enabled by default. If you uncheck the checkbox, the Wi-Fi
Options are disabled, and the Wi-Fi Access Point will not provide or broadcast its Wi-Fi LAN services.
Network Name (SSID)
– preset to a number unique to your unit. You can either leave it as is, or change it by
entering a freeform name of up to 32 characters, for example “Hercule’s Wi-Fi LAN”. On client PCs’ software,
this might also be called the Network Name. The Wi-Fi ID is used to identify this particular Wi-Fi LAN.
Depending on their operating system or client Wi-Fi card, users must either:
• select from a list of available Wi-Fi LANs that appear in a scanned list on their client
• or enter this name on their clients in order to join this Wi-Fi LAN.
Hide Network Name SSID
– If enabled, this mode hides the Wi-Fi network from the scanning features of
Wi-Fi client computers. Hiding the SSID prevents casual detection of your Wi-Fi network by unwanted neigh-
bors and passers-by. The gateway WLAN will not appear when clients scan for access points. If Hide SSID is
enabled, you must remember and enter your SSID when adding clients to the Wi-Fi LAN.
Security, WPA Version
,
WEP Password Length
,
Password
– see
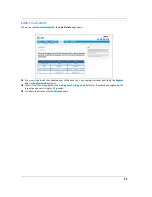
Mode
– The pull-down menu allows you to select and lock the Gateway into the Wi-Fi transmission mode
you want:
B/G/N
,
B-only
,
B/G
,
G-only
, or
N-only.
For compatibility with clients using 802.11b (up to 11 Mbps transmission), 802.11g (up to 20+ Mbps),
802.11a (up to 54 Mbit/s using the 5 GHz band), or 802.11n (from 54 Mbit/s to 600 Mbit/s with the use of
four spatial streams at a channel width of 40 MHz), select
B/G/N
. To limit your Wi-Fi LAN to one mode or the
other, select
G-only
,
N-only
, or
B-only
, or some combination that applies to your setup.
Bandwidth
– use a single 20MHz channel (
20MHz
setting) , or combine two 20MHz channels (
40MHz
set-
ting) to increase data speeds. The 40MHz mode may only be selected if the
Mode
setting is 801.11 B/G/N or
802.11 N-Only. To prevent interference with lower bandwidth clients, the Wi-Fi network will revert to
20MHz operation if non-compatible (802.11B, 802.11G, or 20MHz 802.11N) clients are detected.
Channel
(1 through 11, for North America) on which the network will broadcast. This is a frequency range
within the 2.4Ghz band. The
Automatic
setting allows the Wi-Fi Access Point to determine the best channel
to broadcast automatically.
Power Level
– Sets the Wi-Fi transmit power, scaling down the Wi-Fi Access Point’s Wi-Fi transmit coverage
by lowering its radio power output. Default is
100%
power. Transmit power settings are useful in large ven-
ues with multiple Wi-Fi routers where you want to reuse channels. Since there are only three non-overlap-
ping channels in the 802.11 spectrum, it helps to size the Wi-Fi Access Point’s cell to match the location. This
allows you to install a router to cover a small “hole” without conflicting with other routers nearby.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
is a not a security protocol. It is an easier way to add and securely configure-
new clients to your WLAN.
By default, Privacy is set to Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA-PSK) with a 12 character security key. WPS allows
you to securely share your exact security configuration with a new client that you are adding to the WLAN,
without needing to look up and type this security key. Clients may be added using the WPS button on the
router, or by entering the client WPS PIN on this page.
Network Password
Here you can enter a manual encryption key.
Mode
Will be 802.11
B
only, 802.11
G
only, 802.11
N
only, 802.11
B/G
or 802.11
B/G/N
. These
will vary depending on the
Band
selected.
Bandwidth
The capacity of the Wi-Fi LAN to carry traffic in Megahertz,
20
or
40
.
Channel
The radio channel that your Wi-Fi network is broadcasting on. This should be left at the
default
Automatic
.
Power Level
May be adjusted up to 100%, lower if multiple Wi-Fi access points are in use, and might
interfere with each other.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
May be either
On
or
Off.
NOTE:
While hiding the SSID may prevent casual discovery of your Wi-Fi network, enabling security is the only true
method of securing your network.
NOTE:
If you choose to limit the operating mode to 802.11b or 802.11g only, clients using the mode you excluded
will not be able to connect.
Summary of Contents for NVG595
Page 10: ...Administrator s Handbook 10 ...
Page 65: ...65 ...
Page 68: ...Administrator s Handbook 68 ...
Page 84: ...Administrator s Handbook 84 The following is an example log portion saved as a TXT file ...
Page 90: ...Administrator s Handbook 90 ...
Page 185: ...185 Please visit http www ARRIS com recycle for instructions on recycling ...
Page 210: ...Administrator s Handbook 210 ...
Page 220: ...Administrator s Handbook 218 ...
Page 224: ...Administrator s Handbook 222 ...
Page 226: ...Administrator s Handbook 224 ...