Exercise A
27
To calculate the specific rate constant, k:
The overall mass balance at steady-state condition may be written as:
Input – Output ± Reaction = 0
i.e. for a reactant a in a reactor of volume V
For the continuous reactor operating at steady state the volume may be assumed
constant and
mol/dm
3
sec
The steady state concentration of NaOH in the reactor (a
1
) may be used to calculate
the specific rate constant (k).
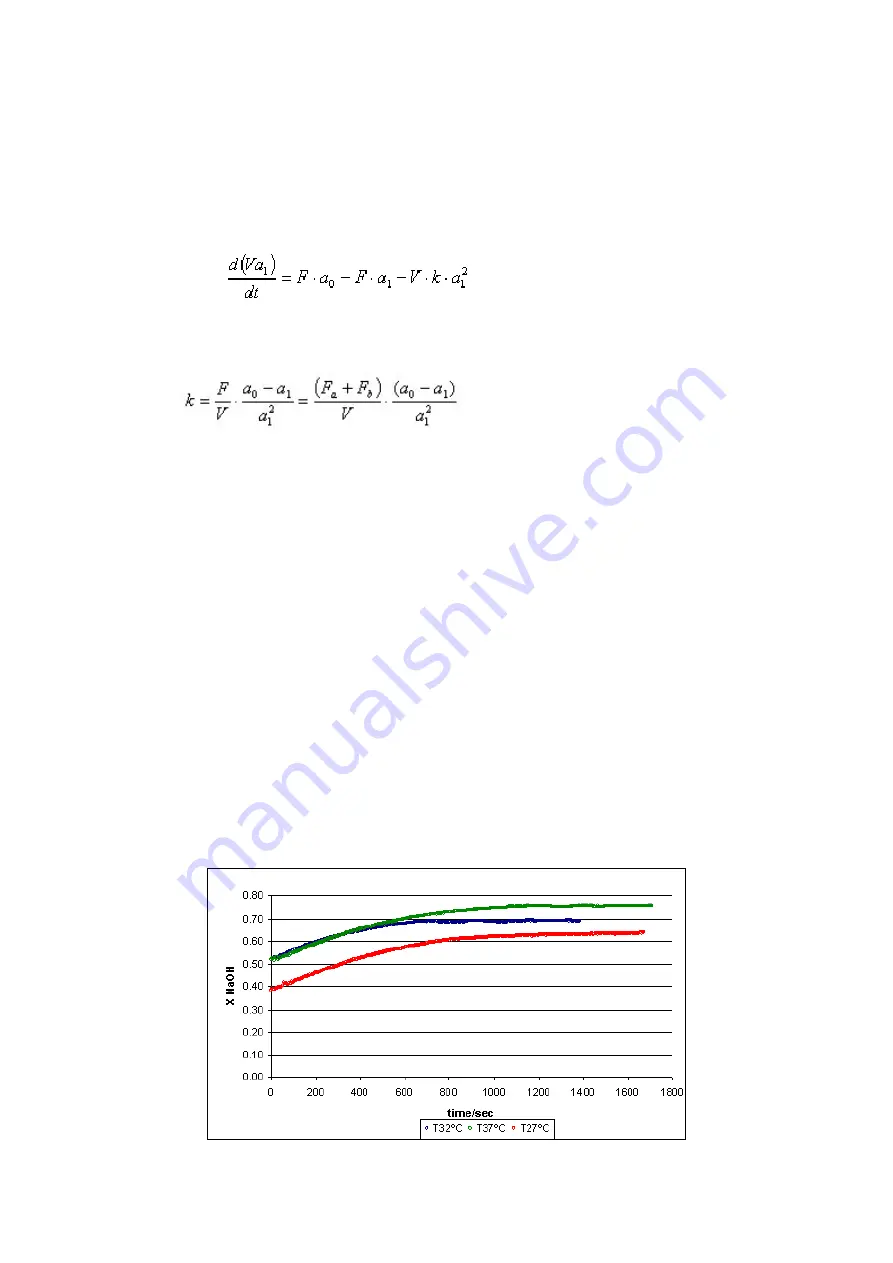
Comment upon the results obtained. How did temperature affect the reaction rate?
and the conversion?
Notes:
1. It is recommended that this experiment should be repeated at various other
temperatures to investigate the relationship between the specific rate
constant (k) and the temperature of reaction. If the reactor temperature is
below ambient Chiller should be required and ‘Experiment with Chiller’ option
should be chosen from the software. See below for examples of experimental
results.
2. It is further recommended that the experiment be repeated using dissimilar
flow rates for the caustic soda and ethyl acetate solutions to investigate the
effect that this will have upon the saponification process.
Treatment Results
Conversion of NaOH at different temperatures:







































