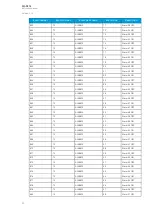
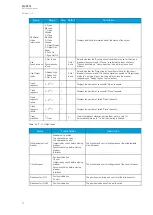
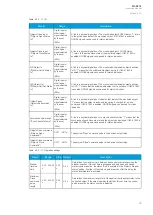
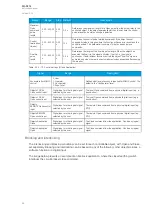
Name Range Step Default
Description
Setting
group
2
0: Not
active
1:
Active
-
0: Not
active
The selection of Setting group 2 ("SG2"). Has the second highest priority input in setting
group control. Can be controlled with pulses or static signals. If static signal
control is applied, no requests with a lower priority than SG1 will be processed.
Setting
group
3
0: Not
active
1:
Active
-
0: Not
active
The selection of Setting group 3 ("SG3"). Has the third highest priority input in setting
group control. Can be controlled with pulses or static signals. If static signal
control is applied, no requests with a lower priority than SG1 and SG2 will be
processed.
Setting
group
4
0: Not
active
1:
Active
-
0: Not
active
The selection of Setting group 4 ("SG4"). Has the fourth highest priority input in setting
group control. Can be controlled with pulses or static signals. If static signal
control is applied, no requests with a lower priority than SG1, SG2 and SG3 will be
processed.
Setting
group
5
0: Not
active
1:
Active
-
0: Not
active
The selection of Setting group 5 ("SG5"). Has the fourth lowest priority input in setting
group control. Can be controlled with pulses or static signals. If static signal
control is applied, SG6, SG7 and SG8 requests will not be processed.
Setting
group
6
0:Not
active
1:Active
-
0:Not
active
The selection of Setting group 6 ("SG6"). Has the third lowest priority input in setting
group control. Can be controlled with pulses or static signals. If static signal
control is applied, SG7 and SG8 requests will not be processed.
Setting
group
7
0: Not
active
1:
Active
-
0: Not
active
The selection of Setting group 7 ("SG7"). Has the second lowest priority input in setting
group control. Can be controlled with pulses or static signals. If static signal
control is applied, only SG8 requests will not be processed.
Setting
group
8
0: Not
active
1:
Active
-
0: Not
active
The selection of Setting group 8 ("SG8"). Has the lowest priority input in setting group
control. Can be controlled with pulses or static signals. If static signal control is applied,
all other SG requests will be processed regardless of the signal status of this setting
group.
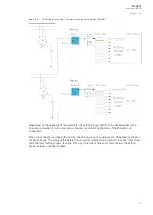
Example applications for setting group control
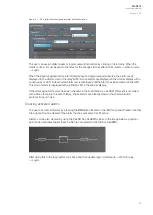
This chapter presents some of the most common applications for setting group changing requirements.
A Petersen coil compensated network usually uses directional sensitive earth fault protection. The user
needs to control its characteristics between varmetric and wattmetric; the selection is based on
whether the Petersen coil is connected when the network is compensated, or whether it is open when
the network is unearthed.
A
AQ
Q-S214
-S214
Instruction manual
Version: 2.04
49