AT-S7/AT-S9 Operations Manual
43
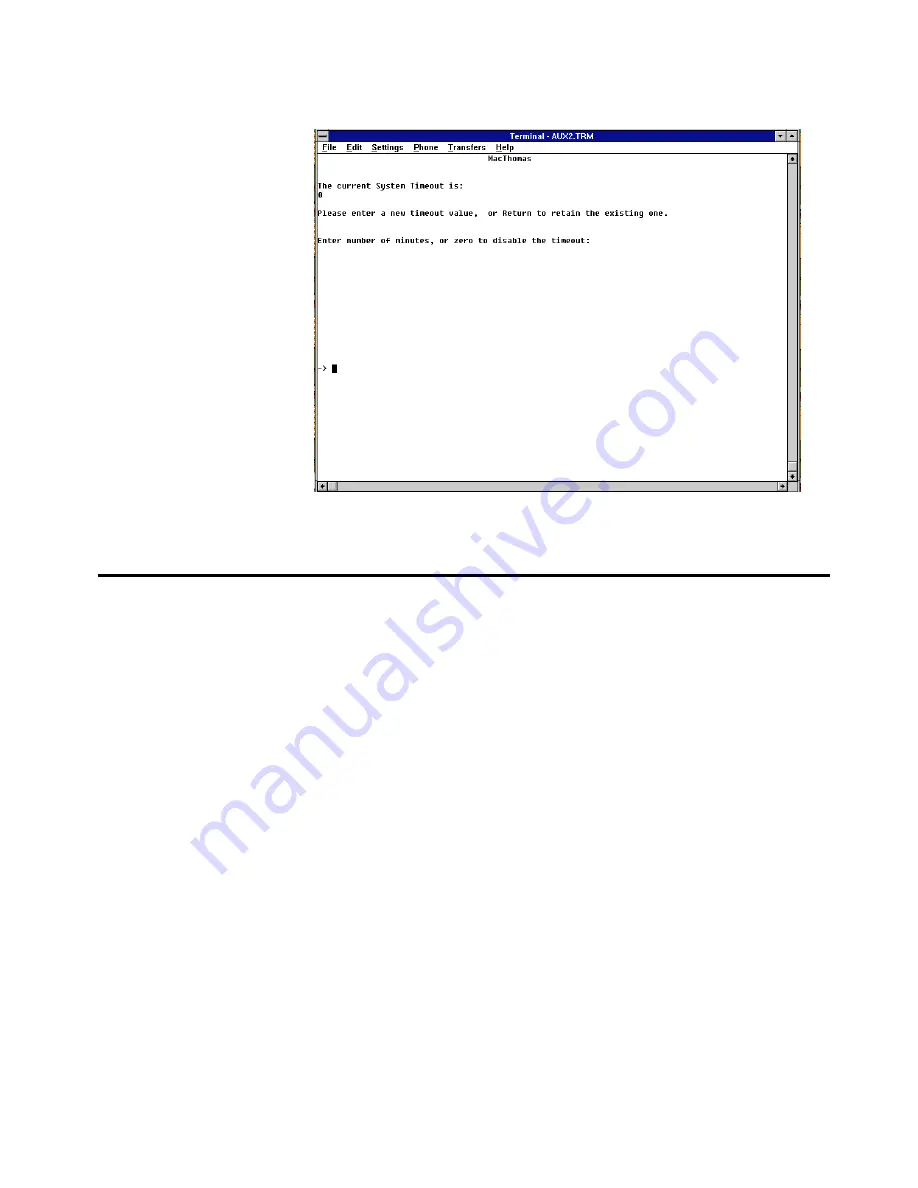
Press
<RETURN>
for the Timeout screen.
The default, “0”, disables the timeout function.
TCP/IP
You must choose a protocol for your network: Is it to be a TCP/IP or a
nonTCP/IP network?
If you have many geographically dispersed subnetworks, each connected to
its own department concentrator, you may want to manage these multiple
switches remotely in a central-site configuration. In this case, TCP/IP
network management may be optimum.
TCP/IP internet addresses consist of user assigned numbers which identify
members of the network. It normally has two fields: network number and
host number. TCP/IP addresses are expressed in the form of a.b.c.d., where
a,b,c and d are each in the 0-254 range. For example, it adheres to the
following notation: 192.136.118.3.
In a nonTCP/IP environment, all switches and devices can be identified by
either any name convention of your choice or by a Media Access Control
(MAC) address (also known as an Ethernet address) which is assigned and
integrated into each switch by the manufacturer. TCP/IP addresses are not
required for local switch management.
















































