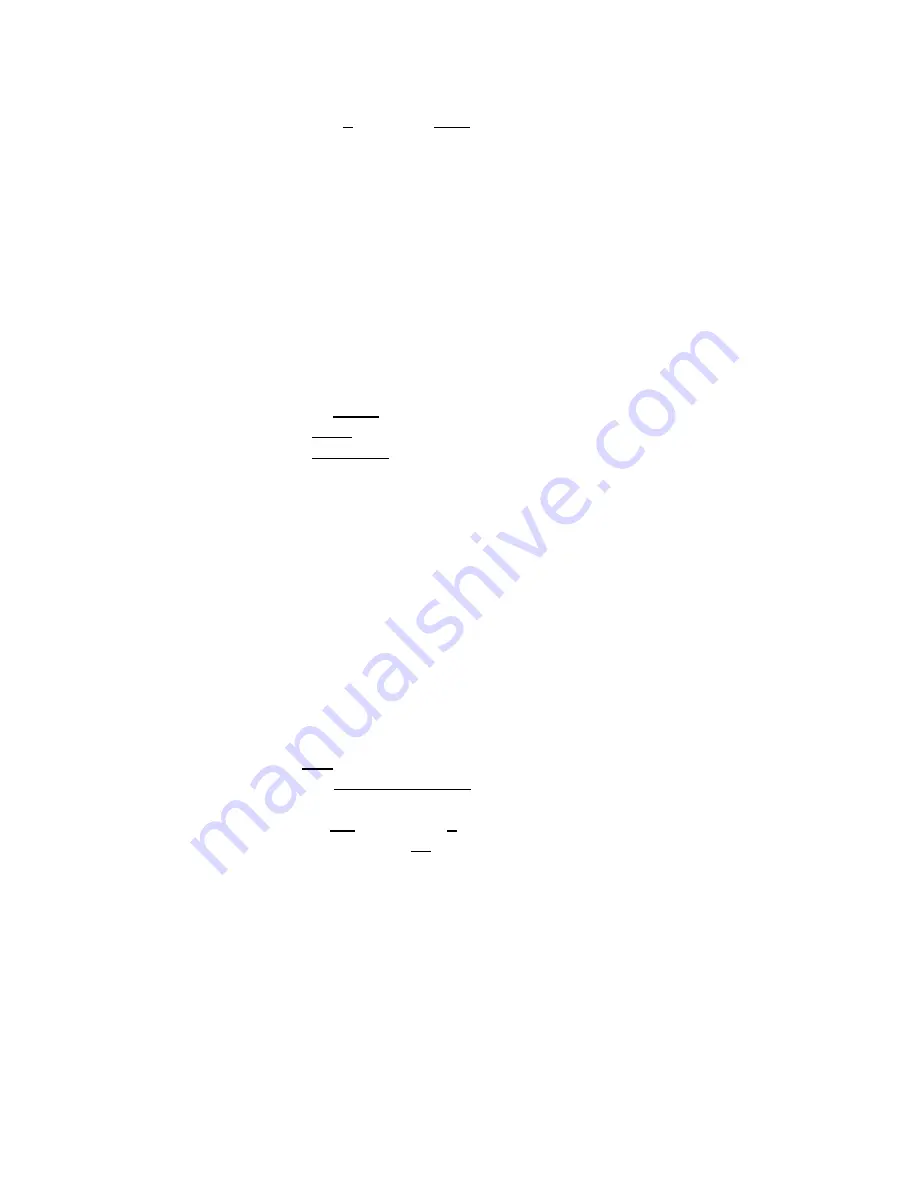
(config-t1 0/2)#tdm-group 1 timeslots 1-24 speed 64
(config-t1 0/2)#no shutdown
(config-t1 0/2)#exit
Configuring the RBS Trunk
Step 1:
First, it is a good idea to create an appropriate Codec List to be used by the PRI
trunk. In a Codec List, you can specify which codec should be prioritized by the
trunk when negotiating the call setup. In this example, a Codec List named
‘Trunk’ is going to be configured to use G.729 as the primary codec and G.711
as the secondary codec.
(config)#voice codec-list Trunk
(config-codec)#codec g729
(config-codec)#codec g711ulaw
(config-codec)#exit
Step 2:
Next, create the RBS voice trunk using the ‘voice trunk’ command and specifying
the type as ‘t1-rbs supervision wink role network’. An optional description can be
given to the trunk as well using the ‘description’ command. The command ‘no
reject-external’ allows the RBS trunk to accept calls from other trunks that may
be configured (i.e. PRI or SIP). This command is necessary for deployments
where more than one trunk is being used (i.e. a SIP trunk and a PRI/RBS trunk to
the CPE). Finally, connect the voice trunk to a TDM group on a T1 interface
using the ‘connect’ statement. The ‘did digits-transferred’ command specifies
how many DNIS digits will be sent to the CPE device on an inbound call.
(config)# voice trunk T02 type t1-rbs supervision wink role network
(config-T02)#description "RBS T1 to PBX"
(config-T02)#no reject-external
(config-T02)#connect t1 0/2 tdm-group 1
(config-T02)#did digits-transferred 10
Step 3:
Since this is a voice trunk and not a voice user, a voice grouped trunk will need
to be configured to specify which numbers should be routed out the RBS trunk.
A good rule of thumb is to be specific with trunks going to CPE devices and be
general when creating call routing rules with trunks going to the PSTN/SIP
network. In this example, we have been assigned the number 256-555-1000 by
the SIP provider and want to route that number out the RBS trunk. We do this by
adding an ‘accept’ entry for the specific number.





























