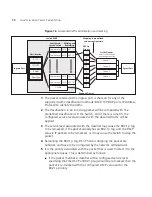
Important QoS Considerations
73
is received has an NBX classifier in it such as the default profile
does, the Switch will automatically detect NBX telephone voice
traffic and prioritize accordingly. The Switch also has an NBX
classifier for Ethernet Type 0x8868, which is the layer 2 NBX traffic.
NBX is layer 2 out of the box and has to be configured by the user
to be layer 3, so the DSCP 46 classifier may in fact be used in fewer
NBX installations than the Ethernet Type 0x8868.
■
Can map between IEEE 802.1D and DSCP to support legacy
devices in the network that only support IEEE 802.1D.
■
Has four traffic queues, but it is important to note that not all
Switches have the same number of priority queues.
■
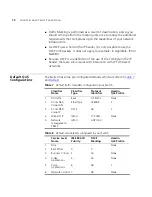
Has six service levels pre-programmed by default as listed in
Table 8
, but up to 900 service levels can be created.
■
Has five Classifiers pre-programmed by default, as listed in
Table 7
.
■
Can only have one QoS profile applied to each port.
■
QoS is about providing a consistent, predictable data delivery service.
It should not be used as an alternative to deploying sufficient
bandwidth. The recommended configuration for most networks is
10/100 Mbps switching to the desktop, Gigabit connections for
servers, and non-blocking Gigabit backbones.
■
QoS requires the support of every network device from end-to-end.
All devices in the network should support QoS. If there is just one
section in the data path that does not support QoS, it can produce
bottlenecks and slowdowns, although a performance improvement
will be noticed over the parts of the network that do support QoS.
■
Ensure that all QoS devices are configured the same way. Mismatches
will cause the same traffic to be prioritized in one section and not in
another. Use a comprehensive QoS management package, such as
3Com Network Supervisor, that will configure all devices in the
network simultaneously and check for errors.
■
Only use Switches or hardware-based routers in the LAN. Hubs cannot
prioritize traffic, and software-based routers can cause bottlenecks.
■
Use Switches and hardware-based routers that understand both the
IEEE 802.1D (incorporating IEEE 802.1p) and DSCP marking schemes.
■
Classify traffic as soon as it enters the network. If traffic is not
classified until it gets to the WAN router or firewall, end-to-end
prioritization cannot be guaranteed. The ideal place for traffic
classification is within the Switch.
Summary of Contents for 3C17205-US - Corp SUPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4400...
Page 8: ...GLOSSARY INDEX...
Page 14: ...14...
Page 26: ...26 CHAPTER 1 SWITCH FEATURES OVERVIEW...
Page 44: ...44 CHAPTER 3 USING MULTICAST FILTERING...
Page 55: ...How STP Works 55 Figure 13 STP configurations...
Page 58: ...58 CHAPTER 4 USING RESILIENCE FEATURES...
Page 84: ...84 CHAPTER 7 STATUS MONITORING AND STATISTICS...
Page 92: ...92 CHAPTER 8 SETTING UP VIRTUAL LANS...
Page 98: ...98 CHAPTER 9 USING WEBCACHE SUPPORT...
Page 120: ...120 CHAPTER 12 POWER MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL...
Page 122: ...122...
Page 126: ...126 APPENDIX A CONFIGURATION RULES...
Page 134: ...134 APPENDIX B NETWORK CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES...
Page 150: ...150 GLOSSARY...