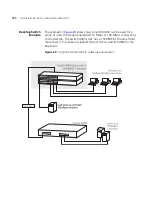
Subnets and Subnet Masks
139
As shown in this example, the 32 bits of an IP address and subnet mask
are usually written using an integer shorthand. This notation translates
four consecutive 8-bit groups (octets) into four integers that range from 0
through 255. The subnet mask in the example is written as
255.255.255.0.
Traditionally, subnet masks were applied to octets in their entirety.
However, one octet in the subnet mask can be further subdivided so that
part of the octet indicates an
extension
of the network number, and the
rest of the same octet indicates the host number, as shown in
Figure 36
.
Figure 36
Extending the Network Prefix
Using the Class B IP address from
Figure 35
(158.101.230.52), the subnet
mask is 255.255.255.240.
The number that includes both the Class B natural network mask
(255.255) and the subnet mask (255.240) is sometimes called the
extended network prefix
.
Continuing with the previous example, the subnetwork part of the mask
uses 12 bits, and the host part uses the remaining 4 bits. Because the
octets are actually binary numbers, the number of subnetworks that are
possible with this mask is 4,096 (2
12
), and the number of hosts that are
possible in each subnetwork is 16 (2
4
).
Subnet Mask Numbering
An alternate method to represent the subnet mask numbers is based on
the number of bits that signify the network portion of the mask. Many
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) now use this notation to denote the
subnet mask. See
Table 17
.
IP address
Network
Subnet and Host
Subnet mask
networ
Host
subn
Subnet
Network
Apply the subnet mask
Result = subnet/host boundary
Take the IP address
1
0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0
0
0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Summary of Contents for 3C17205-US - Corp SUPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4400...
Page 8: ...GLOSSARY INDEX...
Page 14: ...14...
Page 26: ...26 CHAPTER 1 SWITCH FEATURES OVERVIEW...
Page 44: ...44 CHAPTER 3 USING MULTICAST FILTERING...
Page 55: ...How STP Works 55 Figure 13 STP configurations...
Page 58: ...58 CHAPTER 4 USING RESILIENCE FEATURES...
Page 84: ...84 CHAPTER 7 STATUS MONITORING AND STATISTICS...
Page 92: ...92 CHAPTER 8 SETTING UP VIRTUAL LANS...
Page 98: ...98 CHAPTER 9 USING WEBCACHE SUPPORT...
Page 120: ...120 CHAPTER 12 POWER MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL...
Page 122: ...122...
Page 126: ...126 APPENDIX A CONFIGURATION RULES...
Page 134: ...134 APPENDIX B NETWORK CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES...
Page 150: ...150 GLOSSARY...