60
C
HAPTER
8: F
LEXIBLE
I
NTERFACE
C
ARDS
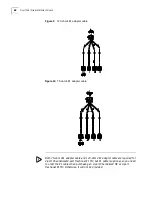
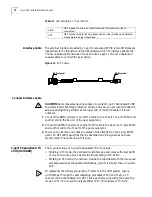
Ethernet cables fit into two categories, i.e., straight-through cables and crossover
cables.
■
Straight-through cable: The sequences of the twisted pairs crimped in the RJ45
connectors at both ends are the same. It is used for connecting a terminal
device (e.g., PC and router) to a HUB or LAN Switch. The cables delivered with
the router are straight-through cables.
■
Crossover cable: The wire sequences of the twisted pairs crimped in the RJ45
connectors at both ends are different. It is used for connecting two terminal
devices (e.g., PC and router).Users can make it as needed.
When preparing network cables, please use shielded twisted-pair (STP) cables so
long they are available for the sake of electromagnetic compatibility.
The interface cables in the standard configuration of FIC cards are
straight-through cables.
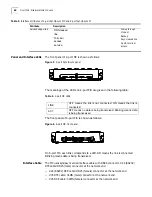
Connect Interface Cable
Use the following procedure to connect interface cable
1
If the Ethernet cable is a straight-through cable, plug one end of the cable into an
Ethernet port on the FIC card, and another end to a HUB or LAN Switch.
2
Power on the Router and check the status of the LINK LED on the FIC panel. ON
means that the link has been connected and OFF means that the link is not
connected. In the latter case, check the line.
CAUTION:
You must connect a cable to the interface with the appropriate mark.
Misplugging is prone to impair the interface card and even damage the router
mainframe.
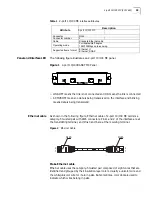
1-port 100 FX MM FIC
(3C13860) and
1-port 100 FX SM FIC
(3C13862)
The 1-port 100FX MM FIC provides one 100Mbps Ethernet multi-mode fiber
interface. The 1-port 100FX SM FIC provides one 100Mbps Ethernet single mode
fiber interface. The high reliability and sound transmission quality intrinsic to
optical fibers enable the 1-port 100FX SM FIC to easily accomplish the
communications between the Router and a LAN. The interface can work in
megabit full-duplex mode.
In terms of transmission mode, optical fibers fall into multi-mode optical fiber and
single-mode optical fiber.
Single-mode optical fiber has very thin core, and transmits only in single mode on
a given wavelength. It features wide band and large transmission capacity.
Multi-mode optical fiber can make the transmission in multiple modes on a given
wavelength. In multi-mode, lights of different modes are transmitted at different
speeds, resulting in phase distortion and hence limiting the transmission band. In
terms of fiber core size, there are two types of multi-mode optical fibers, i.e.,
62.5m and 50m, which are acceptable transmission media in ISO/IEC 11801
standard.
Summary of Contents for 3C13840
Page 18: ...18 CHAPTER 2 INTRODUCING THE ROUTER 6000 FAMILY ...
Page 48: ...48 CHAPTER 5 SOFTWARE MAINTENANCE ...
Page 52: ...52 CHAPTER 6 HARDWARE MAINTENANCE ...
Page 56: ...56 CHAPTER 7 TROUBLESHOOTING ...
Page 78: ...78 CHAPTER 8 FLEXIBLE INTERFACE CARDS ...
Page 82: ...82 APPENDIX A OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT ...