34
ZOLL AED PLUS Administrator’s Guide
Clinical Trial Results for the M Series Biphasic Waveform
The efficacy of ZOLL’s Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform has been clinically verified during a study of
defibrillation of Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)/Ventricular Tachycardia (VT). A feasibility study was
performed initially for defibrillation of VF/VT (n=20) on two separate groups of patients to ensure
waveform safety and energy selection. Subsequently a separate, multi-center, randomized clinical trial
was performed to verify the waveform’s efficacy. A description of this study is provided below. The
study was performed using ZOLL defibrillation systems consisting of ZOLL defibrillators, the ZOLL
Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform and ZOLL Multi-Function Pads.
Randomized Multi-Center Clinical Trial for Defibrillation of Ventricular Fibrillation
(VF) and Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Overview:
The defibrillation efficacy of ZOLL’s Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform was compared to a
monophasic damped sine waveform in a prospective, randomized, multi-center study of patients
undergoing ventricular defibrillation for VF/VT during electro-physiological studies, ICD implants and
test. A total of 194 patients were enrolled in the study. Ten (10) patients who did not satisfy all protocol
criteria were excluded from the analysis.
Objectives:
The primary goal of this study was to compare the first shock efficacy of the 120J
Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform with a 200J monophasic waveform. The secondary goal was to compare
all shock (three consecutive 120, 150, 170J) efficacy of the Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform with that of
a monophasic waveform (three consecutive 200, 300, 360J). A significance level of p=0.05 or less was
considered statistically significant using Fischer’s Exact test. Also, differences between the two
waveforms were considered statistically significant when the customary 95% or AHA recommended
90%* confidence interval between the two waveforms was greater than 0%.
Results:
The study population of 184 patients had a mean age of 63
±
14 years. 143 patients were males.
98 patients were in the biphasic group (ventricular fibrillation/flutter, n=80, ventricular tachycardia,
n=18) and 86 patients were in the monophasic group (ventricular fibrillation/flutter, n=76, ventricular
tachycardia, n=10). There were no adverse events or injuries related to the study.
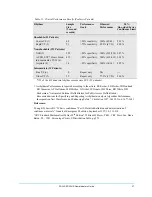
The first shock, first induction efficacy of biphasic shocks at 120J was 99% versus 93% for monophasic
shocks at 200J (p=0.0517, 95% confidence interval of the difference of -2.7% to 16.5% and 90%
confidence interval of the difference of -1.01% to 15.3%).
Successful defibrillation with rectilinear biphasic shocks was achieved with 58% less delivered
current than with monophasic shocks (14
±
1 vs. 33
±
7 A, p=0.0001).
Monophasic
Biphasic
1st Shock Efficacy
93%
99%
p-value
0.0517
95% Confidence Interval
-2.7% to 16.5%
90% Confidence Interval
-1.01% to 15.3%
Содержание Aed Plus
Страница 1: ...Administrator s Guide REF 9650 0301 01 Rev M...
Страница 10: ...x ZOLL AED PLUS Administrator s Guide...
Страница 48: ...38 ZOLL AED PLUS Administrator s Guide...