Reference
Varian, Inc.
User Manual Micro-GC
Page 45
GLOSSARY OF NETWORK TERMS
The following brief glossary of terms may be useful:
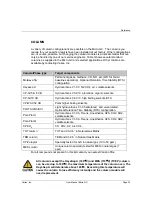
BNC connector
This is a bayonet style connector used for a two-conductor style hardware connection.
BNC connectors are used with the CP-3800 GC.
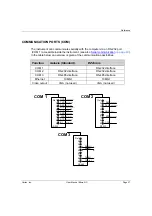
Crossover Cable
A cable is used to connect two, and
only two
, Ethernet devices together.
Domain
This is one of several settings that reside within the TCP/IP configuration that identifies
paths that are used to establish connections with Ethernet devices. The Domain is an IP
address.
Ethernet Address
This is a unique identifier that every Ethernet communication device has assigned to it.
Typically, the Ethernet address cannot be changed and is the permanent way of
identifying a particular hardware device. The Ethernet address consists of 6 pairs of
hexadecimal digits.
Gateway
This is one of several settings within the TCP/IP configuration that identifies paths that
are used to establish connections with Ethernet devices. The Gateway is assigned an
IP Address.
Host name
The host name is an alternate way of identifying a device that is friendlier to people.
Frequently the host name and the IP address may be used interchangeable.
Hub
A device that allows many Ethernet devices to be interconnected. Several hubs may be
interconnected to increase the number of Ethernet connections. For 10Mbits/second
network connections (10BaseT), no more than four (4) hubs may be connected in
series. For 100M bits/seconds network connections (100BaseT), no more then two
hubs may be connected in series.
IP Address
This is a unique number for each Ethernet device within the set of connected devices.
Two PCs may have identical IP addresses so long as they are not interconnected to
each other either through the Internet. The IP Address consists of a series of four sets
of decimal numbers (between 1 and 255) that provide routing information used by the
TCP/IP protocol to establish a reliable connection. Without the IP Address,
communications would be bogged down trying to establish connections to Ethernet
addresses at unknown locations.