5 Installation
12
Installation and maintenance instructions ecoTEC plus 0020214491_01
▶
Note that non-return valves or mixer circuits may be re-
quired in order to eliminate cross-flow to other circuits or
the effects of high temperatures from the cylinder char-
ging circuit.
▶
Connect the cylinder charging pump to the ProE plug X6.
To start up the cylinder charging pump, it is not necessary to
set a diagnostics code. The slot on the PCB is reserved for
the cylinder charging pump.
5.1.3
Cylinder priority switching and heating
circuit via low loss header
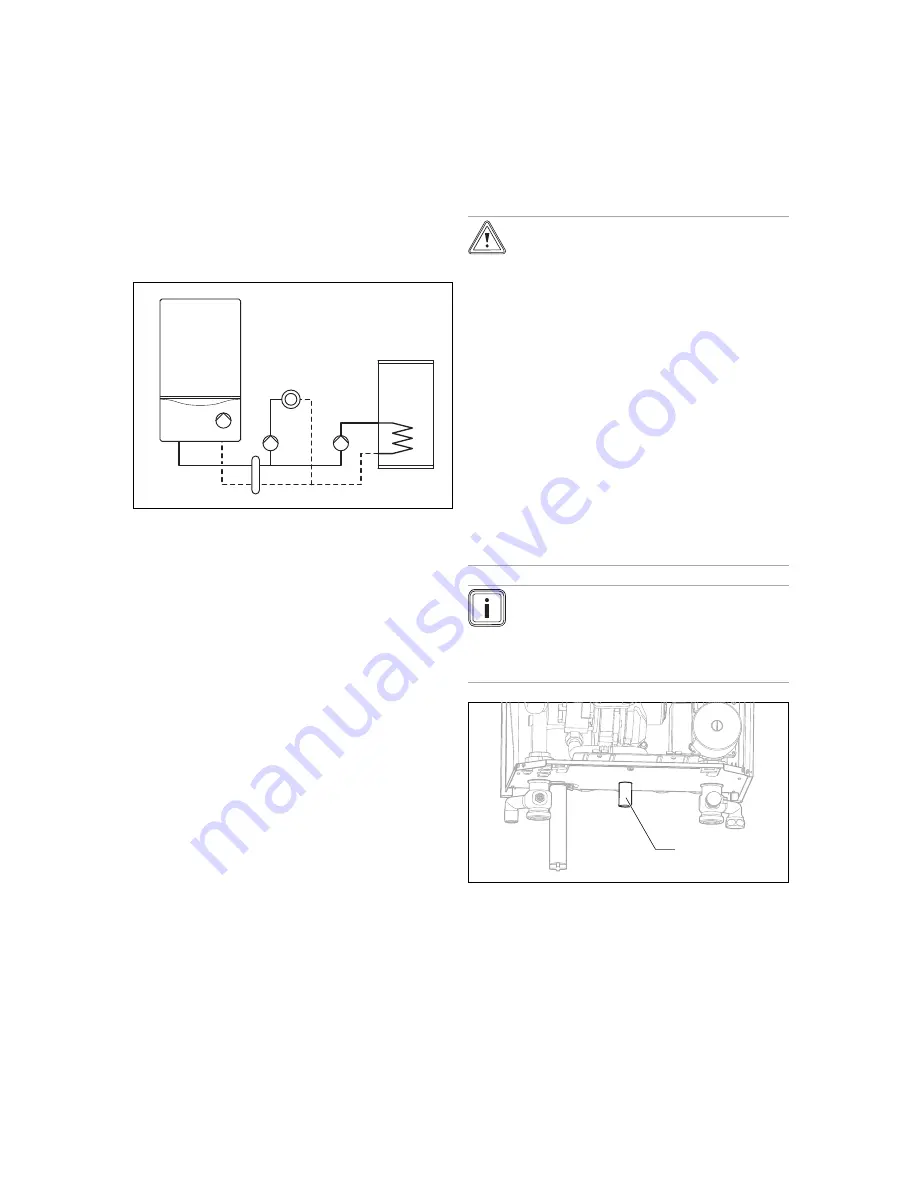
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
Product with internal
pump
2
Low loss header
3
External heating pump
4
Consumer (e.g. heating
circuit)
5
External cylinder char-
ging pump
6
Cylinder
The product's electronics are designed in such a way that
you can connect a standard system (one heating circuit and
one cylinder charging circuit) without the need for special ac-
cessories. If several circuits are required, special accessor-
ies and/or controllers are required. The product's remain-
ing feed head for the low loss header is sufficient. You can
individually design the cylinder charging circuit connection
downstream of the low loss header (cylinder size, cylinder
charging pump size, etc.).
▶
Note that non-return valves or mixer circuits may be re-
quired in order to eliminate cross-flow to other circuits or
the effects of high temperatures from the cylinder char-
ging circuit.
To start up the cylinder charging pump, it is not necessary to
set a diagnostics code. The slot on the PCB is reserved for
the cylinder charging pump.
The settings for the internal pump are made at the factory.
▶
Connect the cylinder charging pump to the ProE plug X6.
▶
Connect the external heating pump to the grey ProE plug
X13.
▶
Set the diagnostics code
D.26
to 2.
5.2
Gas installation
5.2.1
Checking the gas meter
▶
Make sure that the existing gas meter is capable of
passing the rate of gas supply required.
5.2.2
Performing the gas installation
Caution.
Risk of material damage due to the gas
leak-tightness test.
At a test pressure of >11 kPa (110 mbar), gas
leak-tightness tests may cause damage to
the gas valve.
▶
If, during gas leak-tightness tests, you
also place the gas lines and the gas valve
in the product under pressure, use a max.
test pressure of 11 kPa (110 mbar).
▶
If you cannot limit the test pressure to
11 kPa (110 mbar), close any gas isolator
cocks that are installed upstream from the
product before you carry out the gas leak-
tightness test.
▶
If, during gas leak-tightness tests, you
have closed the gas isolator cock that is
installed upstream of the product, relieve
the gas line pressure before you open this
gas isolator cock.
Note
Do
not
reduce the gas pipe dimension down-
stream of the gas meter. Maintain the dimension
right up to the product. Select the correct gas isol-
ator cock. When using an atmospheric sensing
device, select the next-highest pipe cross-section.
1
▶
Install the gas line without tension in accordance with the
recognised rules of technology.
▶
Make sure that the existing gas meter is capable of
passing the rate of gas supply required.
▶
Remove the residues from the gas pipe by blowing
through the gas pipe beforehand.
▶
Screw the gas pipe
(1)
to the (preinstalled) gas isolator
cock so that it is gas-tight. To do this, use the enclosed
compression joint G 1.
▶
Purge the gas pipe before start-up.













































