EVK-NINA-B4 - User guide
UBX-19054587 - R04
Board configuration
Page 20 of 40
C1 - Public
External supply, 3.6
–
1.7 V
When measuring current consumption or performing other NINA-B4 module characterization
measurements, it can be useful to power the module with an external source such as a lab power
supply. In such cases, all jumpers can be removed and the required supply nets can be fed externally
by connecting to the pin headers. For example, the NINA-B4 module can be powered by connecting an
external supply directly to the J22 pin 1 and GND. See also
Using an external power supply or power
analyzer
.
☞
Make sure that unpowered parts of the board are properly isolated from the NINA module. If a
voltage is applied to the signal of an unpowered device/component, current might leak through
various protection circuits of this device. This might give false readings when measuring current
consumption. Isolation can be achieved by removing NINA signal jumpers. See also
Disconnecting NINA signals from board peripherals
.
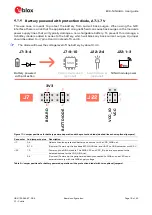
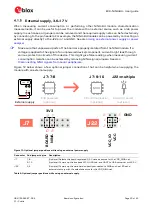
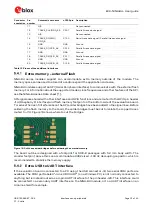
Figure 12 below shows a few optional jumper connections that can be helpful when supplying the
module with an external supply.
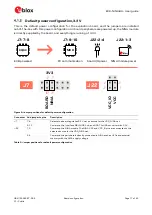
Figure 12: Optional jumper positions while using an external power supply
Connector
Add jumper to pins
Description
J7
7, 8
(Optional) Selects the board regulated 3.3 V net as a source for the VDD_NINA net.
9, 10
(Optional) Powers up the Interface MCU, USB hub, and UART to USB converter with 3.3 V.
J22
3, 4
(Optional) Powers up the peripherals directly connected to NINA such as LEDs and
external memory with the selected source for the VDD_NINA net.
Table 6: Optional jumper positions while using an external supply
J7
B
O
ARD
NINA
3V3
3
4
J22
7
8
9
10
board I/O power
(optional)
J22: multiple
PC communication
(optional)
MCU
DC/DC
EVB powered
(optional)
J7: 9-10
J7: 7-8
V
C
C
_IO
V
C
C
1
2
5
6
GND
-.-- V
External supply