TESTING THE STARTER CIRCUIT:
1. Remove the High voltage cable from the ignition coil and ground it.
2. Move the function switch to Lo-Volt.
3. Connect the black clip to the (-) post.
Note : If the clip is connect to the cable clamp, make sure that the contact is clean and tied before
proceeding to next step.
4. Connect the red clip to the housing of the starter motor. Make sure that a good electrical contact is
made.
5. Crank the engine while watching the meter. If it reads 2 volt or more, the starter motor is poorly
grounded, repair as necessary.
6. Connect the red clip to (+) post.
Note: see step. 3
7. Connect black clip to the isolated terminal of the starter motor.
8. Crank the engine, if meter reads 2V or more, check for loose or dirty connections.
AMMETER FUNCTION
TESTING THE CHARGING CURRENT : (see fig. 6)
1. Disconnect the (-) cable from the battery.
2. Disconnect the wire from the output terminal of the alternator (BAT) and connect the external shunt
between this terminal and the wire just removed.
3. Reconnect the battery cable, crank the engine several times without starting it to partially discharge
the battery.
4. Start the engine, increase the RPM to about 2000 RPM.
Note the reading of the meter.
If it is within 10 AMP of the value specified by the manufacturer. The charging current is OK.
If it is too low proceed to next step to determine if the regulator or the alternator is defective.
5. Refer to steps 2a, b, c of the “testing the charging system” to jump the field terminal of the alternator.
6. Start engine and increase the RPM to 2000 RPM. If the current now is within the value specified, the
regulator is defective; if it is still too low, then the alternator is defective.
POINTS FUNCTION
TESTING THE POINTS RESISTANCE:
1. Connect the black clip to a good electrical ground on the engine. Connect the red clip to the (-)
terminal of the ignition coil.
2. Turn ignition key on; bump the engine until the points are closed.
3 . The pointer of the meter should stay in the OK area, if not the points need to be replaced.
- 5 -
●
Connect read clip to battery positive (+) post, black clip to negative (-) post.
●
Clip the inductive pick up to any of the spark plug cable, preferably as close as possible of the
spark plug without touching any hot metal part.
NOTE:
If the needle does not move or gives an unstable reading when testing engine RPM, proceed as follow:
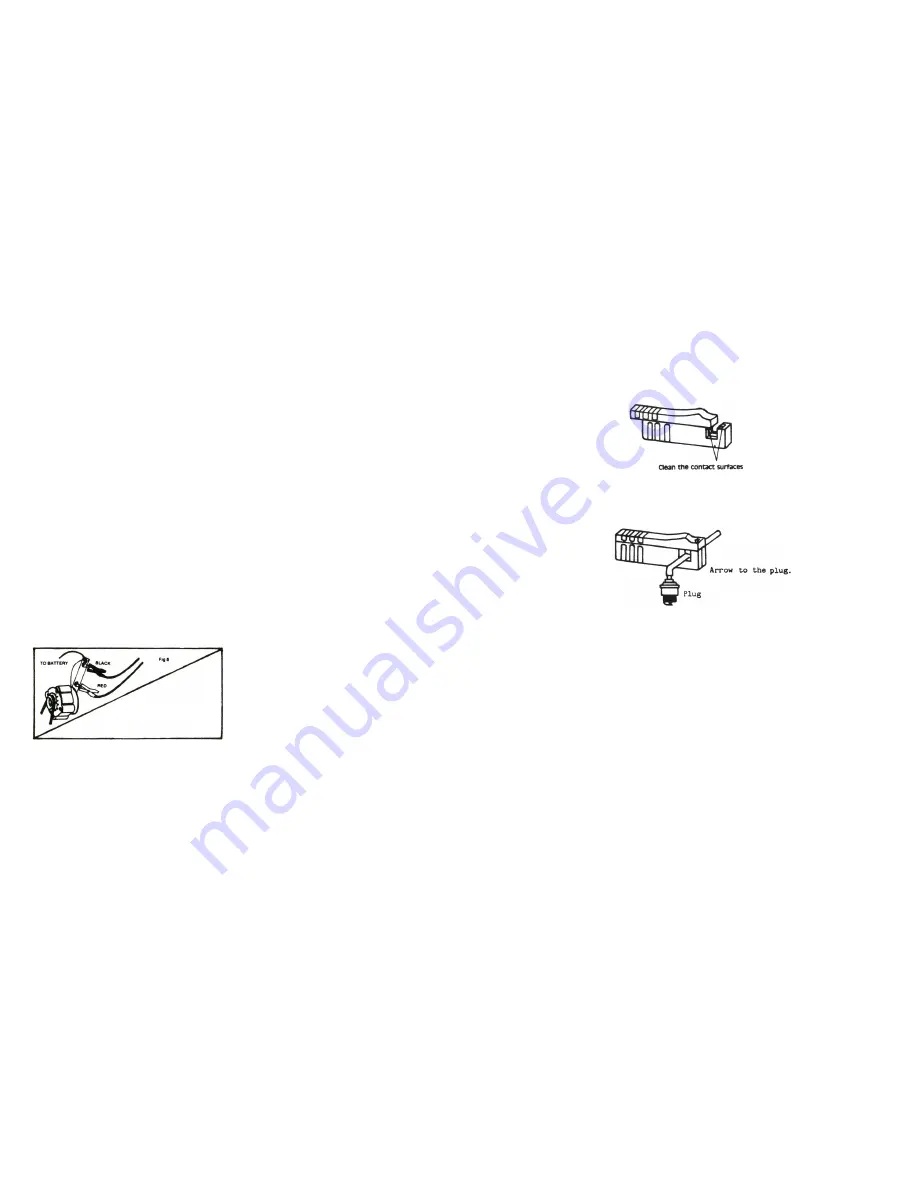
1. Check that the jaws of inductive pickup is fully closed and with the right aide facing the spark plug.
2. Check that the contact surfaces of the upper and lower ferrite cores are clean without dirt or grease.
Use a volatile detergent to clean the contact surfaces if necessary.
3. If the needle still fluctuates, slowly move the inductive pickup along the cable towards distributor cap
and observe reading.
4. If needle fluctuation persists, try another spark plug cable. But it is normal for the needle to fluctuate
slightly at low engine speed.
Note:
Now you are ready to read the RPM of the engine regardless of the number of cylinders.
TEST THE AIR/FUEL MIXTURE:
1. Remove the air filter assembly.
2. Using a flat piece of metal, slowly block off the air intake of the carburetor while watching the RPM:
●
If the RPM does not change until the intake is almost completely blocked off, the air/fuel mixture is
correct.
●
If the RPM increases, the mixture is too lean; if the RPM decreases, the mixture is too rich,
readjust the idle mixture screw accordingly.
TEST THE CONDITION OF THE AIR FILTER:
1. Remove the air filter while watching the RPM, if the RPM varies, the filter is dirty and needs to be
cleaned or replaced.
TEST THE CENTRIFUGAL ADVANCE:
1. Loosen the distributor holdown bolt enough so the distributor can be rotated left and right.
2. Rotate the distributor to get a maximum RPM reading.
3. Increase the RPM to 1000 RPM, again rotate the distributor while watching the RPM; if the RPM can
be increased by 100 or more, the centrifugal advance is faulty, repair or replace as necessary.
TEST THE POSITIVE CRANKCASE VALVE (PCV) :
1. Remove the PCV hose and close off the valve with a finger. Note the RPM, if it drops 50 RPM or
more, the valve is working correctly. If it does not or drops less than 50 RPM, the PCV valve is
plugged or inoperative, repair or replace as necessary.
- 2 -




