EtherCAT Information
Printed in the Federal Republic of Germany
TR-Electronic GmbH 2010, All Rights Reserved
10/07/2013
TR - ECE - BA - DGB - 0080 - 05
Page 101 of 176
4 EtherCAT Information
EtherCAT (
Ether
net for
C
ontrol and
A
utomation
T
echnology) is a
real-time Ethernet
technology
and is particularly suitable for communication between control systems
and peripheral devices such as e.g. I/O systems, drives, sensors and actuators.
EtherCAT was developed in 2003 by Beckhoff Automation GmbH and is available as
an open standard. The "EtherCAT Technology Group" (ETG) user association was
established for the further development of this technology.
EtherCAT is a publicly accessible specification, which was published by the IEC
(IEC/Pas 62407) in 2005 and is part of ISO 15745-4. This part was integrated into the
new editions of the international field bus standards IEC 61158 (Protocols and
Services), IEC 61784-2 (Communication Profiles) and IEC 61800-7 (Drive Profiles
and Communication).
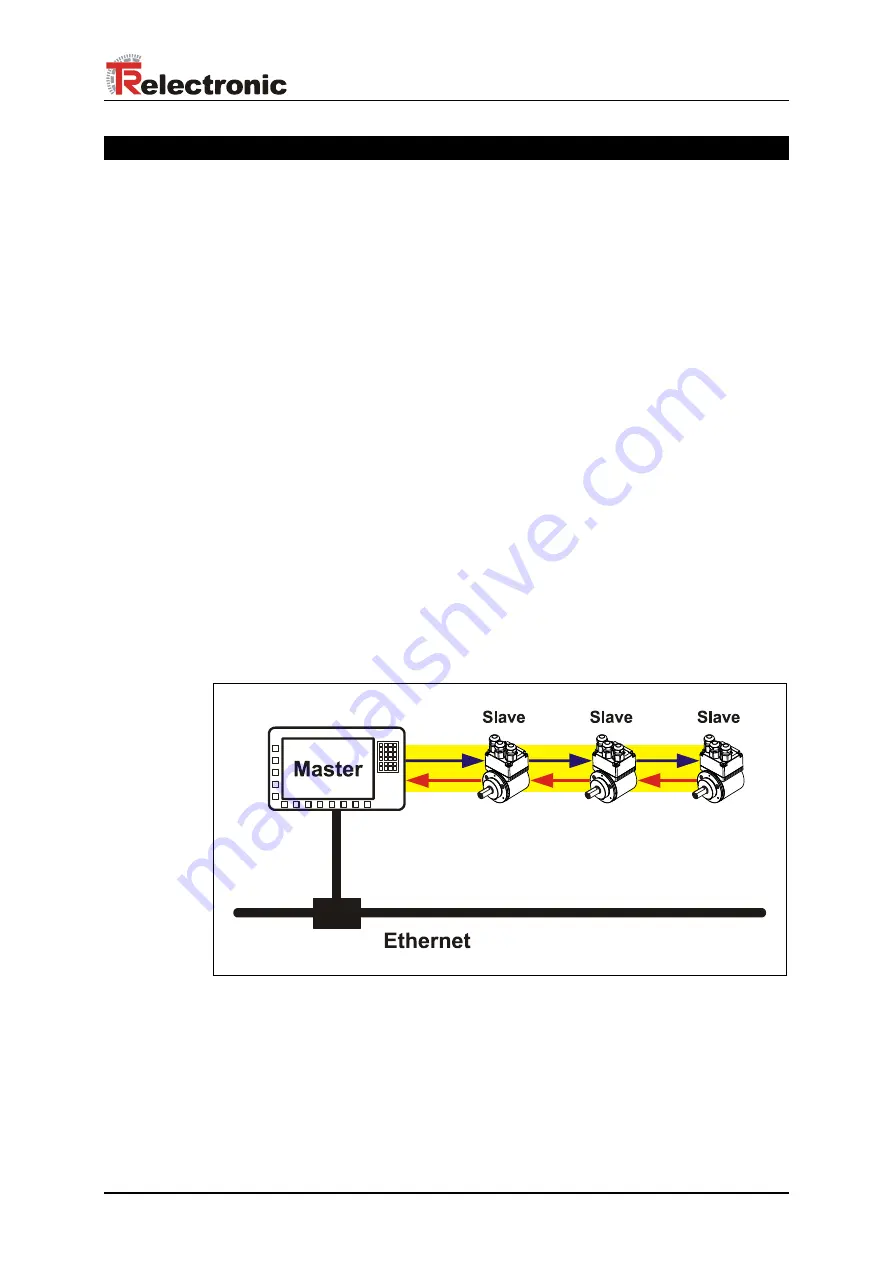
4.1 EtherCAT functional principle
The EtherCAT technology overcomes the generally known limitations of other
Ethernet solutions:
The Ethernet packet is no longer received in each slave first of all, then interpreted
and the process data copied onward. The slave takes the data intended for it, while
the frame passes through the device. Input data are likewise inserted into the frame
as it passes through. The frames are only delayed by a few nano-seconds. The last
slave in the segment sends the now completely processed frame back to the first
slave, which returns the frame to the control as a response frame, so to speak. A
logical ring structure thus results for the communication. As Fast-Ethernet works with
Full Duplex, a physical ring structure also results.
Figure 1: EtherCAT functional principle






























