E6581315
7
4.1. Data transmission format
Note: The term “trip status” used in this manual includes retry waiting status and trip retention status.
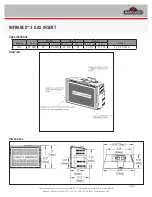
4.1.1. Data transmission format used in ASCII mode
A communication number is used to specify a data item, all data is written in hexadecimal, and JIS-
X-0201 (ASCII (ANSI))-compliant transmission characters are used.
Computer
→
Inverter
Omissible in one-to-one communication For the W and P commands only
Omissible
(3.5bytes
Blank)
"("
(28H)
INV-NO
2 bytes
CMD
1 byte
Communication No.
4 bytes
DATA
0 to 4 bytes
"&"
(26H)
SUM
2 bytes
")"
(29H)
CR
(0DH)
(3.5bytes
Blank)
Checksum area
Omissible
1. “(“ (1 byte)
: Start code in ASCII mode
2. INV-NO (2 bytes) : Inverter number (Omissible in one-to-one communication) ... 00 (30H, 30H) to 99 (39H,
39h), *(2AH)
The command is executed only when the inverter number matches up with that specified
using a parameter.
(When * is specified in broadcast communication, the inverter number is assumed to match
if all numbers except * match. When * is specified instead of each digit (two-digit number),
all inverters connected are assumed to match.)
If the inverter number does not match or if the inverter number is of one digit, the data will
be judged invalid and no data will be returned.
3. CMD (1 byte)
: Command (For details, see the table below.)
4. Communication No.(4 bytes)
: Communication number (See 11, “Parameter data.”)
5. Data (0 to 4 bytes): Write data (valid for the W and P commands only)
6. “&” (1 byte)
: Checksum discrimination code (omissible. When omitting this code, you also need to omit
the checksum.)
7. Sum (2 bytes)
: Checksum (omissible)
Add the ASCII-coded value of the last two digits (4 bits/digit) of the sum of a series of bits
(ASCII codes) from the start code to the checksum discrimination code.
Ex.: (R0000&??) CR
28H+52H+30H+30H+30H+30H+26H=160H
The last two digits represent the checksum. = 60
When omitting the checksum, you also need to omit the checksum discrimination
code.
8. “)” (1 byte)
: Stop code (omissible)
9. CR (1 byte)
: Carriage return code
Details of commands and data
CMD (1 byte)
Write data (0 to 4 bytes) Hexadecimal number
R (52H): RAM read command
W (57H): RAM/EEPROM write command
P (50H) RAM write command
No data
Write data (0 to FFFF)
Write data (0 to FFFF)