TDI T
URBO
T
WIN
FROM
TECH DEVELOPMENT
Publication
T1-321
Page
5
Issued November 15, 2013
Consult your TDI distributor if you have exhaust
plumbing that creates back pressure and reduces starter
performance.
Follow the engine manufacturer’s instructions for starting
the engine.
CAUTION
The grease used in the planetary system has a shelf
life of 2 years. Therefore, if the starter is NOT
installed and operated on the engine for 2 years
after the starter is manufactured, the grease should
be replaced prior to starter operation. The
manufactured date is reflected in the starter serial
number. (Ex: 0602-0567 has a manufactured date
of February 2006.
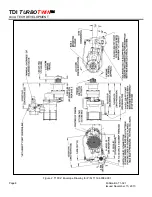
4.1 BASIC OPERATION
The basic operation of the starter follows:
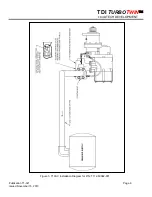
Pressurized air is admitted to the starter’s engagement
piston chamber via the “in” control port by opening the
manual or solenoid valve. The air then translates the
starter’s piston forward allowing the pinion to engage the
engine’s ring gear.
NOTE
40 psi minimum pressure applied to the pre-engaged
piston is required to engage the pinion into the ring.
The forward movement of the piston causes the starter’s
“out” control port to open. Air is then transmitted to the
applied pressure port (APP) on the relay valve causing
the relay valve to open.
Pressurized air is admitted to the starter’s turbine
assembly by the opening of the relay valve. The air
expands through the turbine which produces shaft
rotation and torque. The starter motor torque causes the
engine to accelerate. The fuel and ignition systems now
fire the engine. Closing the relay valve stops the starter.
The operator may decrease starter life by the continual
operation of the starter after the engine has started. After
a successful engine start, turn the air off to the starter
immediately. Minimizing the time the starter is operating
unloaded will maximize starter life. If a start is aborted, a
restart may be attempted after the engine and the starter
have come to rest.
CAUTION
Do not engage the starter while the engine is
running.
The drive air pressure is the primary starter control
parameter
.
It is important, especially on new
installations, to measure this pressure during several
engine starts.
The secondary parameter is the starter pinion speed.
This speed is usually measured by knowledge of the
engine starting speed and the starter cranking ratio. The
cranking ratio is the number of ring
gear teeth divided by the number of pinion teeth. The
starter pinion speed is then found by multiplying the
engine speed by the cranking ratio. The pinion speed is
usually 2000-3500 rpm at typical engine starting speed.
P/N: T112-60082-001 is configured with 15 teeth.
4.2 AUTOMATED START PANEL
The starter drive pressure measured at the starter inlet
will need to be set. As noted above, for maximum life of
the starter pinion and for the protection of the engine ring
gear, limit the operating pressure to that necessary to
start the engine at its most difficult starting conditions.
The speed control parameter will then need to be set.
Engine starting speed along with the cranking ratio
number can be used to determine starter pinion speed.
The pinion speed is usually 2000-3500 rpm for a typical
engine starting speed. Once the start sequence has
begun, the air is admitted to the starter. The starter
begins to accelerate the engine. Once the firing speed of
the engine is reached, the automated start panel may
deliver fuel to the engine. The engine will begin to
accelerate under its own power. The starter should be
dropped out of the sequence at an rpm higher than the
firing speed, but less than the engine idle speed.
The automated start panel should monitor engine speed
to set air on and air off. Do not simply use time as a
control parameter. Avoiding excessive operation of the
starter after the engine is firing will maximize the starter
life.
5.0 STARTER REMOVAL
WARNING
Be sure to bleed pressurized air from reservoir and/or
safety the system by closing the upstream valve to the
starter before starter removal.