Section IV
Multiple UPS Configurations
006-0007129 10/12/2018
Rev B
40 of 60
UPS-1500 3-Phase Guide
www.synqor.com
3-Phase Connection of AC OUTPUTS
Three standard “F” type parallel UPS units can be setup so that their AC OUTPUTS can share
a common “neutral” and deliver output voltages that are phased by 120 degrees (one- third
cycle) from each other. This configuration delivers a 3-Phase OUTPUT where the line-to-neutral
voltage is the rated voltage of the individual UPS units (e.g. 115Vac or 230Vac line-to-neutral)
and the line-to-line voltage is 1.73 times higher (e.g. 200Vac or 400Vac line-to-line).
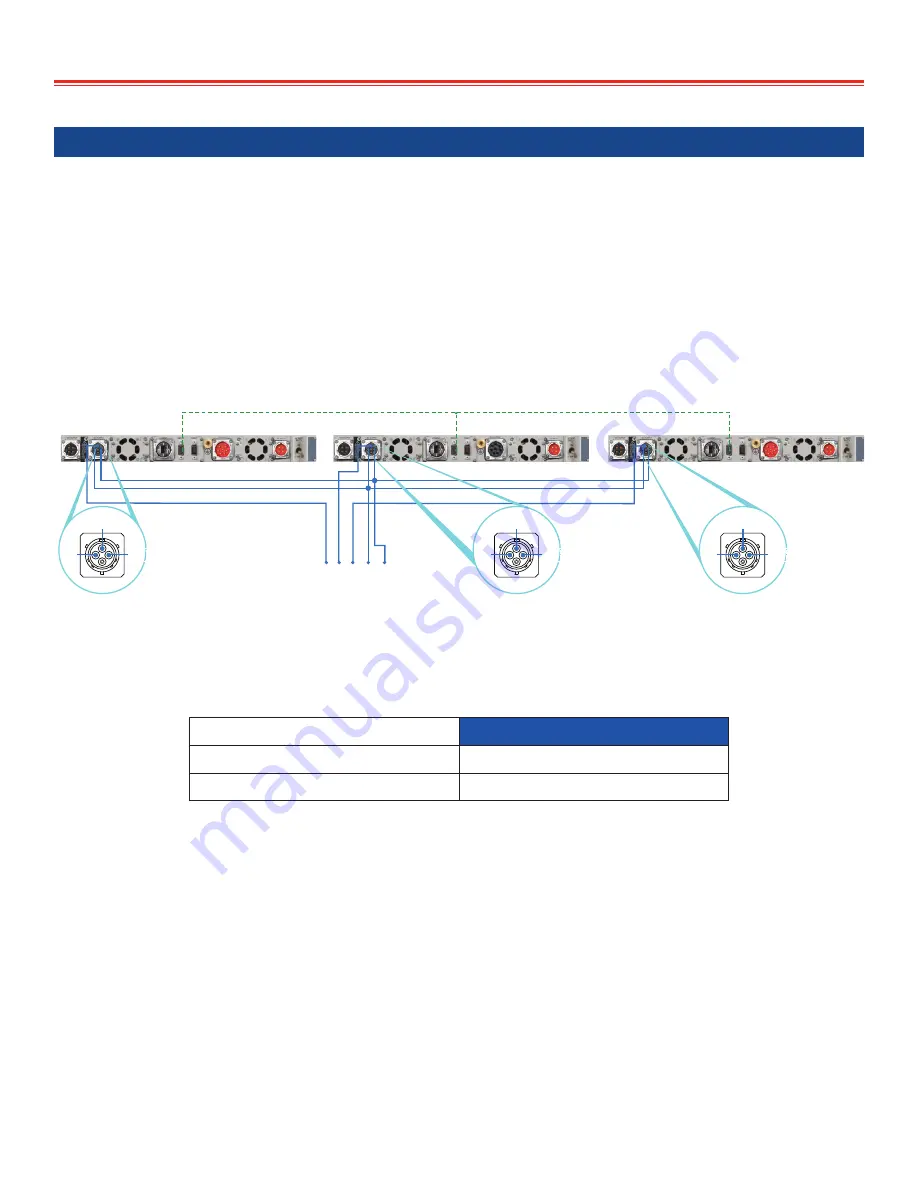
Contact the SynQor factory for N+1 expanded redundant 3-Phase systems. The wiring diagram for the
AC OUTPUT cables and the CONFIGURATION cables for the 3-Phase configuration is shown below:
AC OUTPUT
AC OUTPUT
TO LOAD
AC OUTPUT
L2
N
PEGND
L1
N
PEGND
L3
N
PEGND
REAR PANEL
REAR PANEL
REAR PANEL
Line 2
Line 1
Line 3
L3 N
L2 L1
PEGND
CONFIGURATION cable SYN-9317
If the user is providing the AC OUTPUT cable, all the cable sections should have the
following minimum wire size, depending on whether the AC OUTPUT of the individual UPS
units is 115 Vac or 230 Vac.
UPS AC OUTPUT Voltage
Cable Minimum Wire Size
115 Vac
#14 AWG (2.5 mm
2
)
230 Vac
#16 AWG (1.5 mm
2
)
Note: The “neutral” wire of the 3-Phase AC OUTPUT should be kept at a potential close to
Protective Earth Ground (PEGND).
When ordering, select the “F: Floating” option for UPS units.
Contact the SynQor factory for N+1 redundant 3-Phase systems.
Note: The three connectors of the SYN-9317 CONFIGURATION CABLE are labeled “Line 1”,
“Line 2” and “Line 3”. The UPS unit that receives the “Line 1” connector will have an AC OUTPUT
that is phased 120 degrees (one-third cycle) ahead of the UPS unit that receives the “Line 2”
connector, which in turn will have an AC OUTPUT that is phased 120 degrees (one-third cycle)
ahead of the UPS unit that receives the “Line 3” connector. Connecting the three AC OUTPUTS
to the three line wires of the AC OUTPUT cable in the proper order may be important for some
loads, such as motors.
















































