6
4.
Setup and Operation
Modbus Connections
The ModbusLink-M would be connected to a Modbus Data Master/Logger via either the RS232 or the
RS485 port. There is no need for further battery connections.
From the Modbus sensor’s perspective, the ModbusLink-S replaces the Modbus Master on the remote end of
the connection. The Modbus sensors would connect to the ModbusLink-S just as they would to a Modbus
Master/Logger/ data recorder.
The unit supports Modbus (RTU mode) over RS232 or RS485. A simple command can be used to switch
between RS232 and RS485 modes. The ModbusLink-M module is shipped with a NULL modem so that it
can communicate with a Modbus Master or PLC (RS232 mode only). The ModbusLink-S modules can
interface with a modbus sensor using either the RS232 or RS485 port. No NULL modem is required for
RS232 mode.
ModbusLink Network basics
A ModbusLink network consists of ONLY one master (ModbusLink-M) and one or more slave
(ModbusLink-S) modules with the same
Network-ID
. All slave units must have the same
Network-ID
as
the Master in order to be able to be part of the same network. For the purpose of simplicity, the
Network-ID
can be represented by an imaginary physical wire connecting each
ModbusLink
module to other
ModbusLink
modules (within radio range) having an identical
Network-ID
, in a mesh-like topolog
y.
Multiple networks each with their own Master and Slave(s) can coexist within range of each other, provided
they have unique
Network-IDS
. The default
Network-ID
for all modules (ModbusLink-M and
ModbusLink-S) is ‘15’. No two ModbusLink-M modules with the same
Network-ID
should be within range
of each other.
When the Modbus Logger sends a Modbus command to the ModbusLink-M module, it extracts the address
information from the command and tries to find a ModbusLink-S module with the same address in the
network. If the destination node is not within radio range of the ModbusLink-M module, it will try to
discover a route via intermediate ModbusLink-S modules. If multiple routes are possible to the destination,
the most efficient route will be selected.
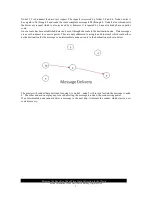
In the above figure, consider the example where the ModbusLink-M module receives a Modbus command
from the Modbus logger addressed to Modbus Sensor #6.The ModbusLink-M broadcasts a route discovery
request to all ModbusLink-S modules in the network. Nodes#2, 3, and 5 receive the discovery request. They
each note that they have a path to M.