Building a Fire
(starting and maintaining a fire)
To start a fire, place several crumpled up balls of
newspaper in the firebox. Place small dry pieces
of kindling on top of the paper, criss-crossing the
kindling so that there are air spaces in between.
Keep the fuel far back enough so that air can
get underneath. Open the air controls fully and
light the newspaper. Once the newspaper and the
kindling is well ignited, close the door. Once the
kindling fire is well established, cord wood can
be added (see
Primary Air Combustion Control
section for proper operation of the air controls).
The unit will burn best with 2-3 pieces of cord
wood spaced 1 to 2 inches apart and allowing air
to get under the fuel. Criss-crossing or arrang-
ing the fuel so that air can get underneath, will
help the fire to get started easily. The unit should
be operated with the air control fully open long
enough to get the cord wood well ignited.
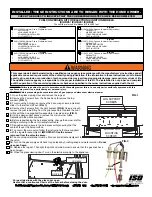
COMBUSTION CONTROLS
Primary Air and Air Boost Controls
There is no flue damper in the wood burning
fireplace. As is common with air tight stoves,
the combustion air control sets the flow of air
Figure 1
entering the firebox. This allows for a more
precise control of the fire. The combustion air
control is located below the door on the left side.
The main source of air (primary air) entering
the firebox can be diminished by moving the
air combustion control from left to right. The
primary air is fully opened when the air control
is completely moved to the left. The air control
device can also be used to add an extra boost of
air especially during fire start up and reloading
of the unit.
Pulling the air combustion control will induce an
air boost at the base of the fire allowing an easier
fire start up. When the fire is well established,
the control can be pushed in to shut down the
air boost allowing for a longer burn time. The
combustion air control should be in the closed
position (primary air and air boost) when the
fireplace is not in use. This will minimize air
leakage up the chimney. The combustion air
control should be opened before opening the
door to minimize the possibility of back draft
coming into the room.
Accelerated Combustion
The maximum heat output for the fireplace is
achieved by burning with the door closed and
the combustion air opened and pulled out. By
this method, the fireplace can produce up to
55,000 BTU of heat per hour. However, it will
be necessary to reload with wood every one or
two hours. This is the least efficient method of
burning the fireplace.
Use caution when firing with the combustion
air control wide open. Only burn cord wood
in this manner. Small dry pieces of softwood
and construction scraps will burn very intensely
using this method and may damage the firebox.
Medium Combustion
This is the recommended mode of operating
the fireplace and should be the one normally
used since it will deposit the least amount of
creosote on the glass and in the chimney. The
combustion air control must be 3/4 closed and
pushed in to close the air boost. The precise
WARNING
Be careful adding wood fuel to
the fire or handling fireplace tools
such as shovels, tongs or pokers.
WARNING
The bottom refractory can be
cracked by excessive abuse such
as tossing heavy logs onto the
grate or gouging with fireplace
tools. Exercise caution when
adding wood to your fireplace.
setting will depend on many factors, including
chimney length and the moisture content of
the wood.
For instance, a long chimney will necessitate
closing the damper more. To obtain the proper
combustion, close the damper completely, then
open it about 1/4” to 1/2”. Three medium size
pieces of wood should be burning on a bed of
hot coals. The heat output will be approximately
30,000 BTU per hour and the loading time will
be about every 3-4 hours. Softwoods may be
burned using this method but the time will be
substantially reduced.
Slow Combustion
When the air combustion control is completely
closed, the fireplace is in a slow combustion phase.
If the hearth is hot enough, slow combustion will
not extinguish the fire, but there will be a notice-
able change in the flame pattern. The flames will
be slow and may appear dirty if the wood is too
wet (moisture content of 20% and more). Do not
allow the wood to burn without flame, since this
will produce excessive creosote in the unit.
Creosote may accumulate on the glass door.
This method of burning should be used only
after operating the fireplace with the air control
opened to produce a hot fire for about an hour
or at medium pace for at least three (3) hours.
Slow combustion can be used at night in order to
reduce the heat output and to prolong the burn.
The loading time will be between 6-8 hours.
REFUELING FOR BEST PERFORMANCE
The fireplace will operate best if attention is
given to operating the unit with the damper
fully opened after refueling in order to bring
the firebox and the chimney system up to their
optimum operating temperature. Combustion
efficiency is relative to firebox temperature. A
temperature of 500º C (932º F) and up, with
a visible flame, in the upper part of the firebox
indicates a maximum efficiency. To obtain this
temperature, the fireplace must be operated
with the primary air and air boost controls fully
opened during 10 to 20 minutes after reloading,
depending on the heat and on the moisture
content of the wood.
Once you have reached the desired temperature,
the air boost can be closed and the primary air
set to a medium setting. You know you have
reached the desired temperature when, closing
the primary air control, you can see a flame
at the top of the firebox. The benefit of this
technique will be cleaner glass, less creosoting,
greater efficiency and the most pleasing fire for
your enjoyment.
Combustion Air Register
Push to Close
Air Boost
Pull to Open
Air Boost
Open
Close
4
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS ARE NOT TO SCALE.