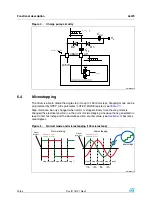
Phase current control
L6470
32/64
Doc ID 16737 Rev 2
7.4 BEMF
compensation
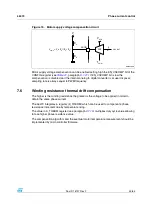
Using the speed information, a compensation curve is added to the amplitude of the voltage
waveform applied to the motor winding in order to compensate the BEMF variations during
acceleration and deceleration (see
).
Compensation curve is approximated by a stacked line with a starting slope (ST_SLP) when
speed is lower than a programmable threshold speed (INT_SPEED) and a fine slope
(FN_SLP_ACC and FN_SLP_DEC) when speed is greater than the threshold speed (see
paragraphs
,
and
).
To obtain different current values during acceleration and deceleration phase two different
final slope values, and consequently two different compensation curves, can be
programmed.
Acceleration compensation curve is applied when the motor runs. No BEMF compensation
is applied when the motor is stopped.
7.5
Motor supply voltage compensation
The sinewave amplitude generated by the PWM modulators is directly proportional to the
motor supply voltage (V
S
). When the motor supply voltage is different from its nominal value,
the motor phases are driven with an incorrect voltage. The L6470 can compensate motor
supply voltage variations in order to avoid this effect.
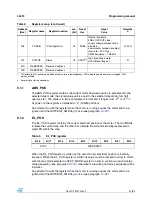
The motor supply voltage should be connected to the integrated ADC input through a
resistor divider in order to obtain V
REG
/2 voltage at the ADCIN pin when V
S
is at its nominal
value (see
).
The ADC input is sampled at f
S
frequency, which is equal to PWM frequency.
Figure 14.
BEMF compensation curve
!-V
3PEED
#OMPENSATION
VALUE
).4?30%%$
34?3,0
&.?3,0?!##
&.?3,0?$%#