43
7G
1,870X2,200
6G
1,500X1,800
2G
370X470
3G
550X650
3.5G
650X830
600X700
5G
1,100X1,250
1,200X1,300
1.52
times
1.96 times
1.73 times
8G
4G
730X920
680X880
2.99
times
2.64
times
The home server’s role—to enable the
enjoyment of entertainment
anywhere in the home
There will soon be a time when high resolution,
large screen, thin flat panel televisions are
common not only in the living room but also
throughout the home. The home server’s role
will be to distribute movies, music, games and
other types of entertainment to each of these
flat panel televisions. The home server will
store a variety of entertainment that can be
downloaded or streamed through the net-
work, then broadcast and distributed to the
various consumer electronics within the
home. It will also act as a network server,
distributing digital photographs and videos
to friends anywhere in the world via the
Internet. The DVD recorder with a hard disk
drive, which was introduced in the fiscal year
ended March 31, 2004, is a precursor to the
home server with its large storage capacity.
Future DVD recorders will incorporate such
advanced technologies as Blu-ray Disc and the
new microprocessor for the broadband era,
Cell, and will evolve into a device capable of
acting as a home server. Along with multi-
function digital television, it will become a
core element of broadband network systems
within the home.
Sony is laying the groundwork to mass-produce
large size LCD panels, a technology considered to be
one of the most important display technologies of
the post-CRT television era. Sony and Samsung
Electronics Co., Ltd., have collaborated to establish
S-LCD Corporation. The joint venture will begin
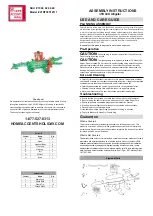
manufacturing the seventh-generation amorphous
silicon TFT LCD display panel, which is primarily
intended for large size flat panel televisions, in April
2005. The glass substrate for these seventh-genera-
tion panels measures 1,870mm x 2,200mm. Each
substrate is expected to produce six large panels for
46 inch televisions, twice as many as the preceding
generation*. These substrates, along with other
technologies, will allow for a highly efficient produc-
tion process. By establishing a stable supply of
panels over the foreseeable future, Sony intends to
actively develop products for the LCD television
market, which is expected to grow steadily in the
years ahead.
* Compared to sixth-generation amorphous TFT LCD
substrates
Sony and Samsung Electronics establish S-LCD Corporation to jointly mass-produce large size LCD panels
The evolution of rear-projection
television
In the fiscal year ended March 31, 2004, Sony’s
Grand Wega LCD rear-projection television,
particularly the larger models with 60 inch to
70 inch screens, was a huge success in the U.S.
market. Two key reasons for its popularity were
its larger screen and lower power consumption.
In the fiscal year ending March 31, 2005, Sony
will introduce a newly developed high resolution
digital cinema projector equipped with the newly
developed SXRD, a high resolution LCD display
device, in the U.S. market. It will be marketed as a
commercial-use projector, targeting cinemas and
multi-purpose halls, where there is a strong
demand for higher resolution images. In the
future, Sony plans to incorporate this device into
its household LCD projection televisions.
Home Electronics
Mobile Electronics
Game
Entertainment
Financial Services
Other
DVD recorder Sugoroku
Super Audio CD/DVD
Grand Wega
Comparison of different generations of glass substrates
(Unit: mm)
Overview of S-LCD
Capital:
2.1 trillion won (Samsung Electronics:
50% +1 share, Sony: 50% –1 share)
Location: Tangjeong, Republic of Korea
Product:
Amorphous silicon TFT LCD display panel
(principally for large screen televisions)
Capacity: 60,000 panels per month