1-9
BBBB
Pla
y
bac
k
35
Follow the procedure
1
–
4
on page 34.
“Memory Stick”
•
Operation is not guaranteed if you are using a “Memory Stick” that was formatted with a
personal computer, or if you used a personal computer to format the “Memory Stick” in your
camera through a USB connection.
•
Do not optimize the “Memory Stick” on a Windows machine. This will shorten the “Memory
Stick” life.
•
Do not compress the data on the “Memory Stick.” Compressed files cannot be played back on
your camera.
6
Select and double-click the desired image file from the folder.
For the detailed folder and file name, see “Image file storage destinations and
image files” on page 37.
∗
Copying a file to the hard disk of your personal computer before viewing it is
recommended. If you play back the file directly from the “Memory Stick”, the image
may break off.
For Macintosh users
5
Double click the newly recognized icon on the desktop.
The folders inside the “Memory Stick” are displayed.
6
Select and double-click the desired image file from the folder.
Notes on using your personal computer
Desired file type
Double-click in this order
Still image
“Dcim” folder
t
“100msdcf” folder
t
Image file
Moving image*
“Mssony” folder
t
“Moml0001” folder
t
Image file*
Clip Motion
image
“Dcim” folder
t
“100msdcf” folder
t
Image file
E-mail image
TIFF image
(uncompressed)
“Mssony” folder
t
“Imcif100” folder
t
Image file
36
For Windows Me and Windows 2000 users
The following procedures are recommended when disconnecting the USB cable from
your personal computer or ejecting the “Memory Stick” from the camera while it is
connected to your personal computer.
1
Stop the drive by clicking on the “Unplug/Eject” icon in the task tray.
2
When the message appears confirming the safe removal of the hardware,
disconnect the USB cable or eject the “Memory Stick”.
Software
•
Depending on your application software, the file size may increase when you open a still image
file.
•
When you load an image modified using the supplied retouch software from your personal
computer to the camera or when you directly modify the image on the camera, the image
format will differ so the “FILE ERROR” message may appear and you may be unable to open
the file.
•
Depending on your application software, only the first frame of the Clip Motion file may be
played back.
Communications with your personal computer (for Windows
only)
Communications between your camera and your personal computer may not recover after
recovering from Suspend, Resume, or Sleep.
BBBB
Pla
y
bac
k
37
Image file storage destinations and
image files
Image files recorded with your camera are grouped in folders by recording mode.
The meanings of the file names are as follows.
ssss
stands for any number
within the range from 0001 to 9999.
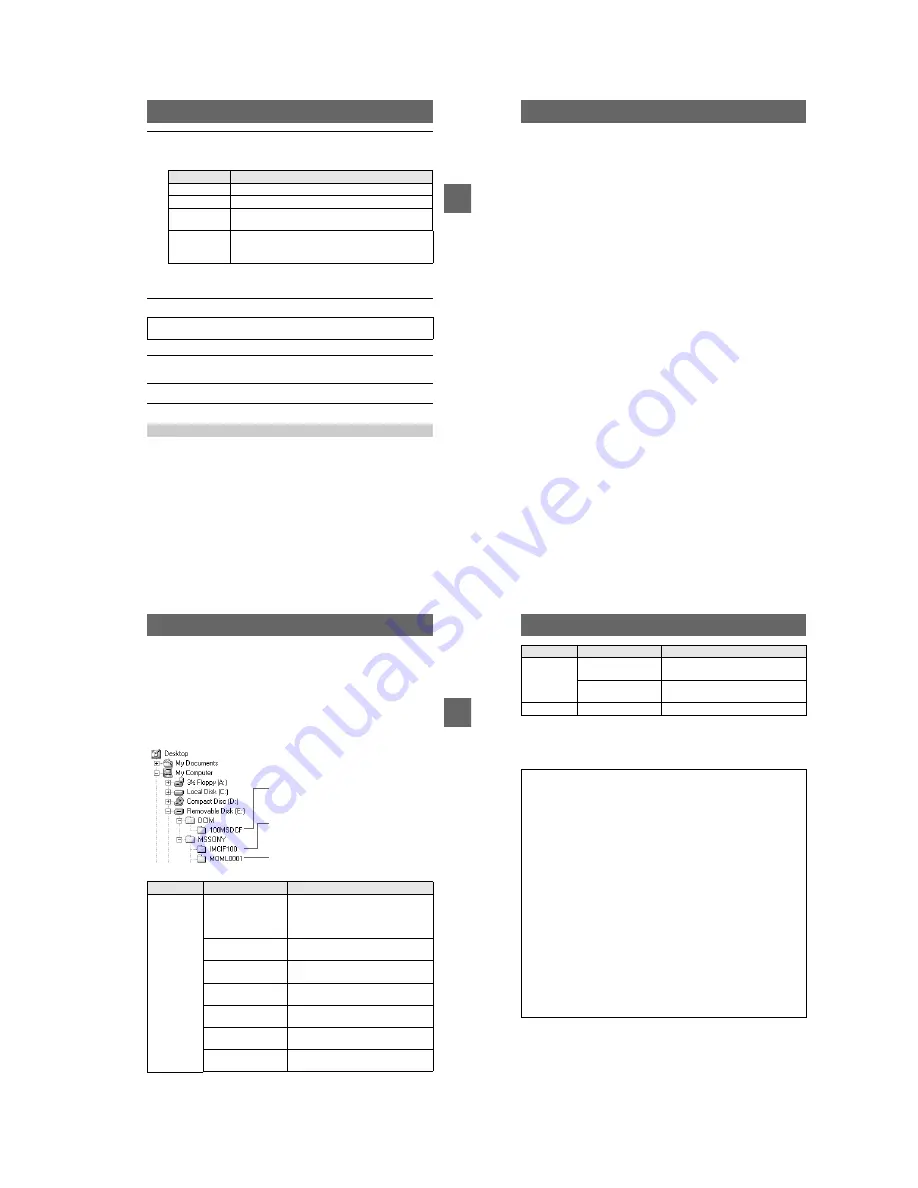
For Windows Me users (The drive recognizing the camera is
“E.”)
Folder
File
Meaning
100MSDCF
DSC0
ssss
.JPG
•
Still image file recorded normally
•
Still image file recorded in
– E-MAIL mode (page 48)
– TIFF mode (page 50)
CLP0
ssss
.GIF
•
Clip Motion file recorded in NORMAL
mode (page 51)
CLP0
ssss
.THM
•
Index image file of Clip Motion file
recorded in NORMAL mode
MBL0
ssss
.GIF
•
Clip Motion file recorded in MOBILE
mode (page 51)
MBL0
ssss
.THM
•
Index image file of Clip Motion file
recorded in MOBILE mode
TXT0
ssss
.GIF
•
Still image file recorded in TEXT mode
(page 49)
TXT0
ssss
.THM
•
Index image file of still image file
recorded in TEXT mode
Folder containing still image, TEXT mode image
and Clip Motion image data
Folder containing E-MAIL mode and TIFF mode
image data
Folder containing moving image data
38
The numerical portions of the following files are the same.
– A small-size image file recorded in E-MAIL mode and its corresponding image file
– An uncompressed image file recorded in TIFF mode and its corresponding image file
– An image file recorded in TEXT mode and its corresponding index image file
– An image file recorded with Clip Motion and its corresponding index image file
IMCIF100
DSC0
ssss
.JPG
•
Small-size image file recorded in
E-MAIL mode (page 48)
DSC0
ssss
.TIF
•
Uncompressed image file recorded in
TIFF mode (page 50)
MOML0001
MOV0
ssss
.MPG
•
Moving image file recorded normally
Tips
The digital still camera saves recorded images as digital data. The format of the
saved data is called as the file format. The formats that can be used with this
camera are as follows:
JPEG format
Most digital still cameras, operating systems of computers, and browser
software adopt this format. This format is able to compress files without
appreciable deterioration. However, if the image is compressed and saved on
repeated occasions, the image will deteriorate. This camera records still images
using the JPEG format for normal recording.
GIF format
Using this format, the image will not deteriorate even if the image is compressed
and saved on repeated occasions. This format limits the number of colors to
256 colors. This camera records still images using the GIF format in Clip
Motion (page 51) or TEXT mode (page 49).
TIFF format
Stores shooting images without compression, so the image does not deteriorate.
Most of operating systems and applications correspond to this format. This
camera records still images using the TIFF format for the TIFF mode (page 50).
MPEG format
This format is very typical for moving images. This camera records moving
images using the MPEG format.
Folder
File
Meaning






























