21 / 44
Siemens
VAV compact controller KNX/PL-Link G..B181.1E/KN
CE1P3547en
Building Technologies
2017-03-23
4.2 Electrical installation / cabling
4.2.1 Power supply cabling
The permissible cable lengths and cross-sectional areas depend on the actuators’
current draw and the voltage drop on the connecting lines to the actuators. The
necessary cable lengths can be determined from the following chart or with the
help of the formulas. Cf. also to technical data in section
8
.
When determining the cable length and the cross-sectional area, it is to ensure that
the permissible tolerances of the actuators’ operating voltage are adhered to, in
addition to the permissible voltage drop on the power supply and signal lines (see
table below).
The cables are to be sized depending on the type of actuator used and based on
the following data:
Type
Operating voltage
Line
Max. permissible
voltage drop
GDB181 / GLB181
AC 24 V
G0, G
each 4 % (tot. 8 %)
The power supply voltage drop at AC 24 V must not exceed 8 % (4 % over the G0).
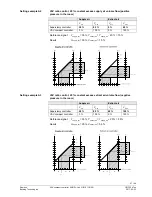
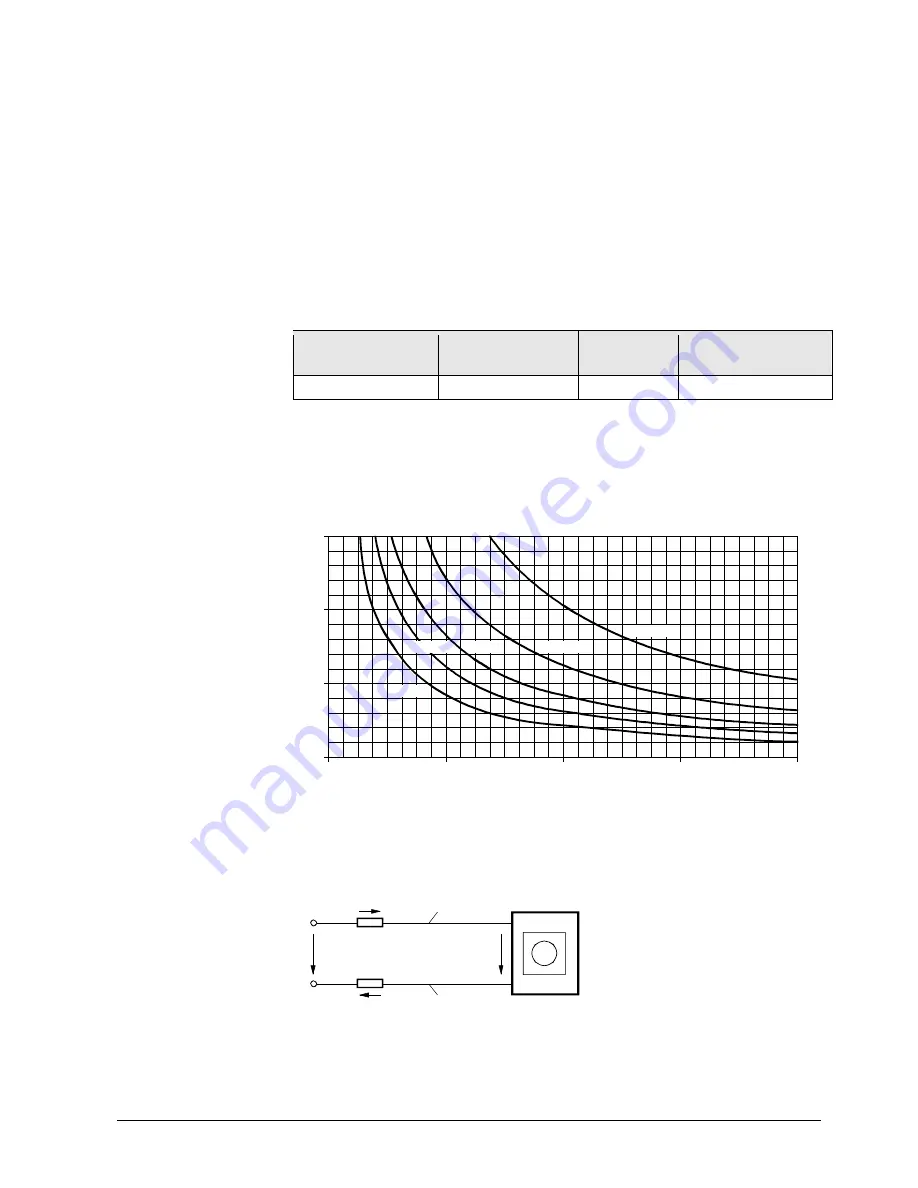
The chart below applies to AC 24 V operating voltage and shows the permissible
cable length
L
as a function of power
P
, and the cross-sectional areas as a
parameter.
300
200
100
0
0
8
16
24
32
L
[m]
P
[VA, W]
2.5 mm²
1.5 mm²
1 mm²
0.5 mm²
0.75 mm²
46
1
4D
0
1e
n
The values in [VA, W] on the P-abscissa are allocated to the permissible voltage
drops (
Χ
U/2U = 4 %) on line length L as per the above table and the basic diagram.
P is the decisive power consumption of all actuators connected in parallel.
U
Χ
U/2
Χ
U/2
R
L
R
L
L
L
U
,Χ
U
46
1
4D
0
9
M
Permissible cable
lengths and cross-
sectional areas
Note
Permissible voltage drop
Note
L/P chart for
AC 24 V
Note on chart
Basic diagram:
Voltage drop on the
supply lines