7SR210 & 7SR220 Applications Guide
2.5
Sensitive Earth-fault Protection (50SEF)
Earth fault protection is based on the assumption that fault current levels will be limited only by the earth fault
impedance of the line and associated plant. However, it may be difficult to make an effective short circuit to earth
due to the nature of the terrain e.g. dry earth, desert or mountains. The resulting earth fault current may therefore
be limited to very low levels.
Sensitive earth fault (SEF) protection is used to detect such faults. The RM range of relays have a low burden, so
avoiding unacceptable loading of the CTs at low current settings.
SEF provides a backup to the main protection. A DTL characteristic with a time delay of several seconds is
typically applied ensuring no interference with other discriminative protections. A relatively long time delay can be
tolerated since fault current is low and it is impractical to grade SEF protection with other earth fault protections.
Although not suitable for grading with other forms of protection SEF relays may be graded with each other.
Where very sensitive current settings are required then it is preferable to use a core balance CT rather than wire
into the residual connection of the line CTs. The turns ratio of a core balance CT can be much smaller than that of
phase conductors as they are not related to the rated current of the protected circuit. Since only one core is used,
the CT magnetising current losses are also reduced by a factor of 3.
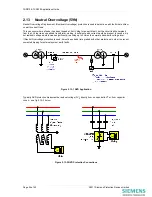
Circuit 1
Circuit 2
Circuit 3
Core
Balance
CT
INCOMER
Figure 2.5-1 Sensitive Earth Fault Protection Application
There are limits to how sensitive an SEF relay may be set since the setting must be above any line charging
current levels that can be detected by the relay. On occurrence of an out of zone earth fault e.g. on circuit 3 the
elevation of sound phase voltage to earth in a non-effectively earthed system can result in a zero sequence
current of up 3 times phase charging current flowing through the relay location.
The step change from balanced 3-phase charging currents to this level of zero sequence current includes
transients. It is recommended to allow for a transient factor of 2 to 3 when determining the limit of charging
current. Based on the above considerations the minimum setting of a relay in a resistance earthed power system
is 6 to 9 times the charging current per phase.
©2011 Siemens Protection Devices Limited
Page 17 of 40