12
AK - 44
CHASSIS
This Current Sense pin senses the voltage developed on the series resistor R806 inserted in the source of the power
MOSFET. When I sense reaches 1V, the Driver output (pin 5) is disabled. This is known as the Over Current Protection
function. A 200mA current source is flowing out of the pin 3 during the start–up phase and during the switching phase
in case of the Pulsed Mode of operation. A resistor can be inserted between the sense resistor and the pin 3, thus a
programmable peak current detection can be performed during the SMPS stand–by mode.
8.5 Standby Operation
As mentioned earlier the Start–up Management of MC44608 is as follows:
The Vi pin 8 of IC800 is directly connected to the HV DC rail Vin. This high voltage current source is internally connected
to the VCC pin and thus issued to charge the VCC capacitor. The V CC capacitor charge period corresponds to the
Start–up phase. When the V CC voltage reaches 13V, the high voltage 9mA current source is disabled and the device
starts working. The device enters into the switching phase.
To help increase the application safety against high voltage spike on pin8 a small wattage 1k _ series resistor is inserted
between the Vin rail and pin 8. After this start-up the IC can distinguish between the different modes of operation using
the following technique:
8.6 Mode Transition
The LW latch is the memory of the working status at the end of every switching sequence. Two different cases must be
considered for the logic at the termination of the SWITCHING PHASE:
1. No Over Current was observed
2. An Over Current was observed
These two cases correspond to the two signals “NOC” in case of “No Over Current” and “OC” in case of Over Current.
The effective working status at the end of the ON time memorized in LW corresponds to Q=1 for no over current, and
Q=0 for over current.
To enter the standby mode secondary side is reconfigured using D889 loop, this starts with the microprocessor ‘s pin 47
becomes high; as the standby port becomes high Q503 conducts and Q802 becomes off then D889 conducts and the
high voltage output value becomes lower than the NORMAL mode regulated value. The shunt regulator IC118 is fully
OFF. In the SMPS stand–by mode all the SMPS outputs are lowered except for the low voltage output that supply the
wake–up circuit located at the isolated side of the power supply. In that mode the secondary regulation is performed by
the Zener diode (D801) connected in parallel to the TL431. The secondary reconfiguration status can be detected on
the SMPS primary side by measuring the voltage level at pin4 of TR802.
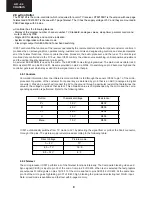
In the SMPS stand–by mode the 3 distinct phases are:
The SWITCHING PHASE: Similar to the Overload mode. The current sense clamping level is reduced. When VCC
crosses the current sense section, the C.S. clamping level depends on the power to be delivered to the load during the
SMPS stand–by mode. Every switching sequence ON/OFF is terminated by an OC as long as the secondary Zener
diode voltage has not been reached. When the Zener voltage is reached the ON cycle is terminated by a true PWM
action. The proper SWITCHING PHASE termination must correspond to a NOC condition. The LW latch stores this
NOC status. The LATCHED OFF PHASE: The MODE latch is set.
The START–UP PHASE is similar to the Overload Mode. The MODE latch remains in its set status (Q=1).
The SWITCHING PHASE: The Stand-by signal is validated and the 200uA is sourced out of the Current Sense pin 2.
8.7 SMPS Switch Off
When the mains is switched OFF, so long as the electrolytic bulk capacitor provides energy to the SMPS the controller
remains in the switching phase. Then the peak current reaches its maximum peak value, the switching frequency
decreases and all the secondary voltages are reduced. The V CC voltage is also reduced. When VCC is less than 6,5V,
the SMPS stops working
9. LINE CIRCUIT
Line and frame drive are generated by IC403. The sync pulses are separated from the incoming video signal at pin 18/
20/22 and used to control the internal circuitry of the IC. Line drive is produced by counting down the external 4.43 MHz
crystal at pin 40 to 15.625 KHz locked to the incoming sync. This drive is output on pin 48 and feeds directly to the line
drive transistor Q601. Note. That the output of IC403 Pin 48 is an open-collector and requires a pull up resistor, if the pin
is open circuited for test no waveform will be seen. Q601 collector feeds the line output transistor Q603.
The line output stage is conventional with a transformer containing a split diode winding for EHT generation. Fifth
harmonic tuning is achieved by capacitor C618/619.
A fly-back pulse is taken from pin 1 of the FBT transformer. This is required by IC403 (Pin 49) for burst / sync gating, and
RGB line blanking. The ver_sync signal is output from the pin47 and fed to Pin41 of IC501. The H_sync pulse is taken
from pin 1 of the FBT and fed to the micro at pin 40. These two signals are required by the micro for graphics timing and
also for text.
Содержание 21LT-45SES
Страница 6: ...6 21LT 45S CHASSIS LAYOUT Mother Unit CRT Unit ...
Страница 44: ...32 AK 44 CHASSIS 18 2 Schematic Diagram of Video Circuit 1 I H G F E D C B A 2 3 4 5 6 7 Page 33 ...
Страница 45: ...33 AK 44 CHASSIS 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 I H G F E D C B A Page 32 18 2 Schematic Diagram of Video Circuit ...
Страница 46: ...34 AK 44 CHASSIS 1 I H G F E D C B A 2 3 4 5 6 7 Page 35 18 3 Schematic Diagram of SMPS Circuit ...
Страница 47: ...35 AK 44 CHASSIS 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 I H G F E D C B A Page 34 18 3 Schematic Diagram of SMPS Circuit ...
Страница 48: ...36 AK 44 CHASSIS 1 I H G F E D C B A 2 3 4 5 6 7 18 4 Schematic Diagram of Audio Circuit ...
Страница 49: ...37 AK 44 CHASSIS 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 I H G F E D C B A 18 5 Schematic Diagram of Deflection Circuit ...
Страница 50: ...38 AK 44 CHASSIS 1 I H G F E D C B A 2 3 4 5 6 7 Page 39 18 6 Schematic Diagram of Scart AV Front Circuits ...
Страница 52: ...40 AK 44 CHASSIS 1 I H G F E D C B A 2 3 4 5 6 7 18 7 Schematic Diagram of CRT Socket Circuit ...
Страница 55: ...43 AK 44 CHASSIS Notes ...