EN
Multiprocess 175. Operating manual.
Multiprocess 175. Operating manual.
21
20
Correct work preparation
The method of preparation of components to be welded will depend on
equipment available and relative costs. Methods may include sawing,
punching, shearing, lathe cut-offs, flame cutting and others. In all
cases edges should be prepared for the joints that suit the application.
The following section describes the various joint types and areas of
application.
4.6 Types of joints
This system is capable of several types of weld, from Butt through to
Fillet welds.
5. General welding information.
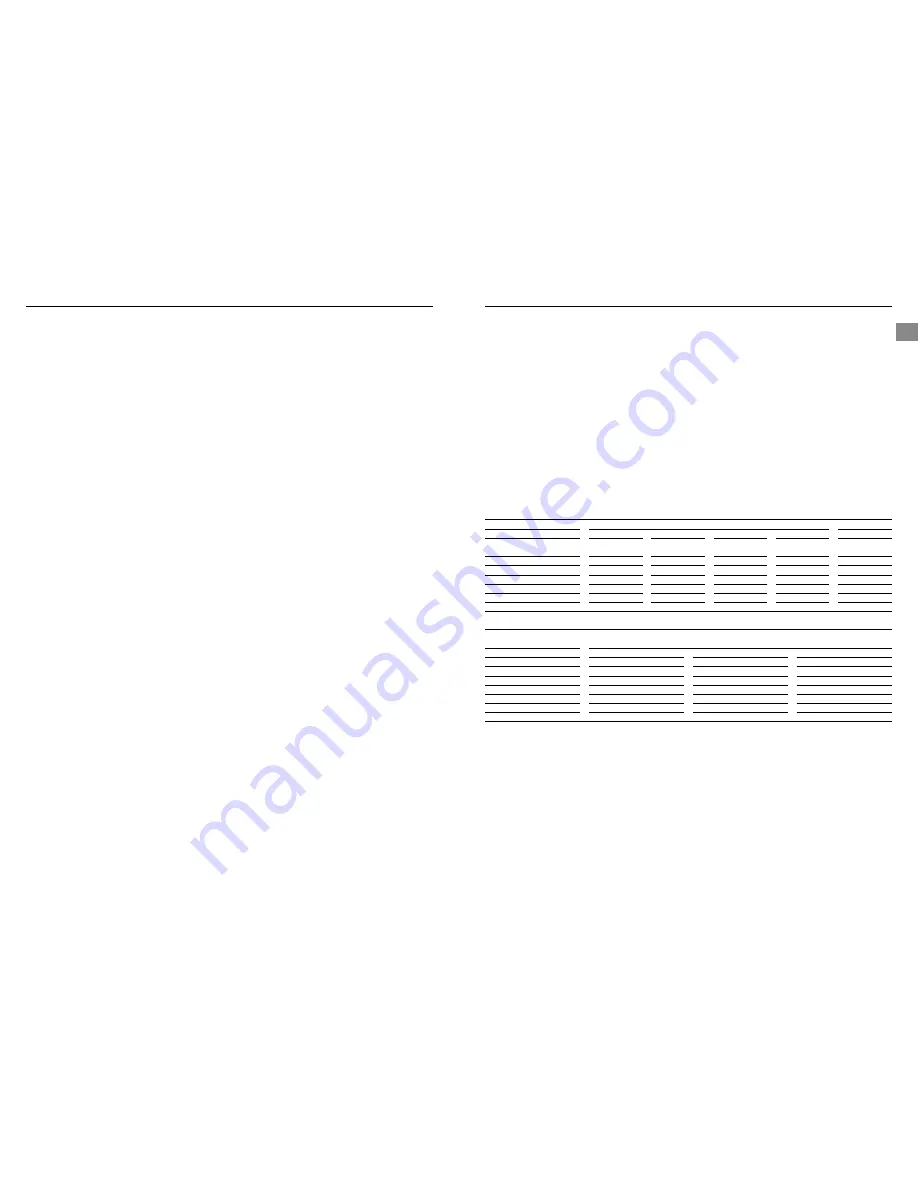
5.1 Recommended welding parameters for MIG/MAG
ARGOSHIELD LIGHT™ or CORGON 5S2™
Indicative welding parameters
Dip transfer
Spray transfer
Material thickness (mm)
Welding position
Wire diameter (mm)
Current (amps)
Voltage (volts)
Wire feed speed (m/min)
Gas rate flow (L/min)
Travel speed (mm/min)
1–1.6
Horizontal /
Vertical
0.8–0.9
45–80
14–16
3.5–5.0
15
350–500
2
Horizontal /
Vertical
0.8–0.9
60–100
16–17
4.0–7.0
15
350–500
3
Horizontal /
Vertical
0.8–0.9
80–120
16–18
4.0–7.0
15
320–500
4
Horizontal /
Vertical
0.9–1.0
80–150
16–18
4.0–7.0
15
280–450
3
Horizontal
0.8
160–180
23–25
7.5–9.0
15
800–1000
STAINSHIELD MIG™ or CRONIGON 2™
Indicative welding parameters
Dip transfer
Material thickness (mm)
4
6
8
Welding position
Wire diameter (mm)
Current (amps)
Voltage (volts)
Wire feed speed (m/min)
Gas rate flow (L/min)
Travel speed (mm/min)
Horizontal / Vertical
0.9–1.0
100–125
17–19
5.0–6.5
15
400–600
Horizontal / Vertical
0.9–1.0
120–150
18–20
6.0–7.5
15
280–500
Horizontal / Vertical
0.9–1.0
120–150
18–20
6.0–8.0
18
280–450





















