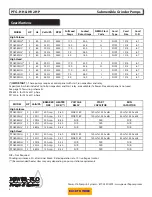
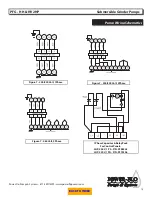
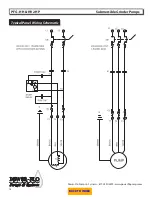
Power-Flo Pumps & Systems • 877-24PUMPS • www.powerfl opumps.com
9
Pre-Operation
1. Check Voltage and Phase
Compare the voltage and phase
information stamped on the pump
name
plate.
2.
Check Pump Rotation
- Improper
motor rotation can result in poor
pump performance and can damage
the motor and/or pump. Check
rotation on three phase units by
momentarily applying power and
observe
the
“kickback”.
Kickback should always be in a
counter-clockwise direction as
viewed from motor end or opposite
to impeller rotation. Incorrect rotation
for Single-Phase pumps is unlikely.
If the rotation is incorrect contact
factory.
3.
Name Plate
- Record the information
from the pump name plate to
drawing in front of manual for future
reference.
4.
Insulation Test
- An insulation
(megger) test should be performed
on the motor. Before the pump is put
into service. The resistance values
(ohms) as well as the voltage (volts)
and current (amps) should be
recorded.
5.
Pump-Down Test
- Be sure pump
has been properly wired, lowered into
the basin, sump or lift station, check
the system by filling with liquid and
allowing the pump to operate through
its pumping cycle. The time needed to
empty the system, or pump-down
time along with the volume of water,
should be recorded.
Maintenance
No lubrication or maintenance is required.
Perform the following checks when pump
is removed from operation or when pump
performance deteriorates:
a). Inspect motor chamber for oil level
and
contamination.
b). Inspect impeller and body for
excessive build-up or clogging.
c). Inspect motor and bearings.
d). Inspect seal for wear or leakage.
Servicing
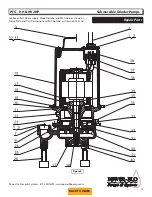
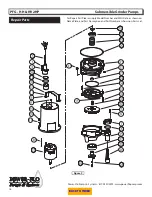
NOTE: Item numbers in ( ) refer to Figures
8 & 9.
Cooling Oil -
Anytime the pump is
removed from operation, the cooling oil
in the motor housing should be checked
visually for oil level and contamination.
To check oil, set unit upright. Remove
pipe plug (4) from housing (15). With a
flashlight, visually inspect the oil in the
housing (15) to make sure it is clean and
clear, light amber in color and free from
suspended particles. Milky white oil
indicates the presence of water. Oil level
should be just above the motor when
pump is in vertical position.
Oil Testing
• Drain oil into a clean, dry container by
placing pump on it’s side, remove pipe
plug (5), from housing (15).
• Check oil for contamination using an
oil tester with a range to 30 Kilovolts
breakdown.
• If oil is found to be clean and
uncontaminated (measuring above
15 KV. breakdown), refill the housing.
• If oil is found to be dirty or
contaminated (or measures below
15 KV. breakdown), the pump must
be carefully inspected for leaks at the
shaft seal, cable assembly, square ring
and pipe plug, before refilling with oil.
Tolocate the leak, perform a pressure
test.
After leak is repaired, dispose of old oil
properly, and refill with new oil.
Pressure Test (If oil has been drained)
Remove pipe plug (4) from housing (15).
Apply pipe sealant to pressure gauge
assembly and tighten into hole. Pressurize
motor housing to 10 P.S.I. Use soap
solution around the sealed areas and
inspect joints for “air bubbles”.
If, after five minutes, the pressure is still
holding constant, and no “bubbles” are
observed, slowly bleed the pressure and
remove the gauge assembly. Replace
oil. Leek must be located and repaired if
pressure does not hold.
Pressure Test (If oil has NOT been
drained) -
Oil should be at normal level.
Remove pipe plug (4) from housing (15).
Apply pipe sealant to pressure gauge
assembly and tighten into hole. Pressurize
motor housing to 10 P.S.I. Use soap
solution around the sealed areas above the
oil level and inspect joints for “air bubbles”.
For sealed areas below oil level, leeks will
seep oil. If, after five minutes, the pressure
is still holding constant, and no “bubbles” /
oil seepage is observed, slowly bleed the
pressure and remove the gauge assembly.
Replace oil. Leek must be located and
repaired if pressure does not hold.
Installation & Service
Figure 2
PFG - HH & HV 2HP
Submersible Grinder Pumps
BACK TO INDEX