4-12
4 Making Measurements
Optimizing the
RF bandwidth
The input of the vibrometer is equipped with an RF band-pass filter (refer to
). To achieve optimal adaptation to the FM-signal bandwidth, the
RF bandwidth is automatically adjusted according to the velocity
measurement range set. As this process also affects the input signal of the
displacement decoder, the setting of the velocity measurement range is
relevant, even if only the displacement output is being used.
The signal-to-noise ratio of the displacement measurement can be improved
with targeted limitation of the RF bandwidth which is particularly important in
the case of weak optical signals. This means that the velocity measurement
range should be selected to be as low as the application allows. The
maximum velocity must not exceed the respective full scale range i.e. 10
times the scaling factor (e.g. 50 mm / s for the measurement range 5
). If
the L
ED
VELOCITY OVER lights up continuously or the displacement signal
breaks down, the next highest velocity measurement range has to be
selected.
If however the optical signal is constantly good, the range 1,000
should
be selected as it does not limit the bandwidth and therefore its influence does
not need to be taken into consideration.
Using the
CLEAR
function
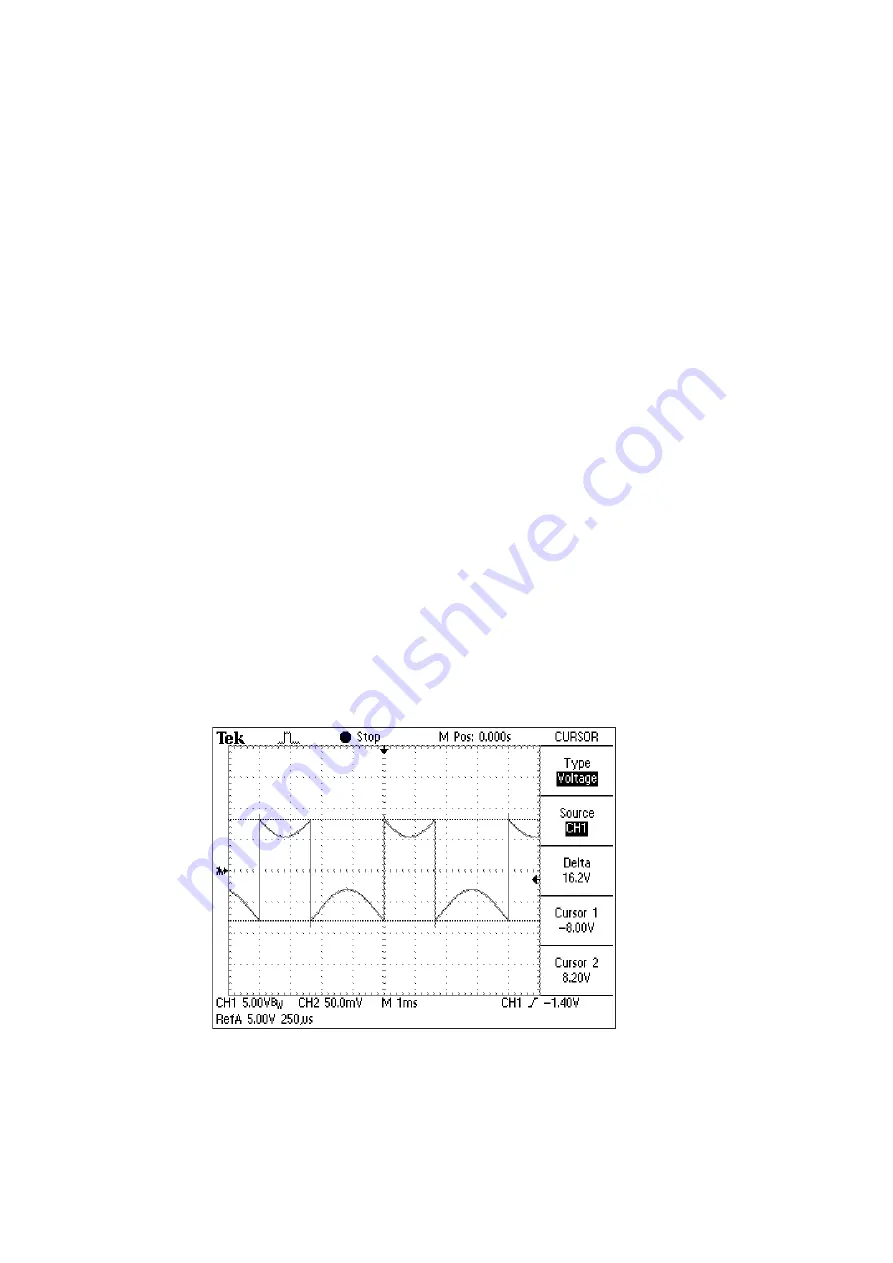
As there is no lower frequency limit for the displacement decoder, it can also
measure stationary signals (DC). After setting a certain displacement
measurement range, a certain voltage is present at the output (the so-called
DC offset) which depends on the distance of the object to the sensor head
and on the thermal drift of the interferometer. Dynamic displacements of the
object (AC) are correctly added to or subtracted from this DC offset as long as
the output voltage does not exceed
±
8 V. Otherwise the output voltage will
jump from the positive end of range to the negative and vice versa as the
internal counter overflows (refer to
), and as a result the AC
signal is distorted. This is shown as an example in the oscilloscope trace in
.
mm
s
----------
V
⁄
mm
s
----------
V
⁄
Figure 4.7: Displacement signal when the counter overflows due a DC offset
















































