SEBU8337
47
Maintenance Section
Re
fi
ll Capacities
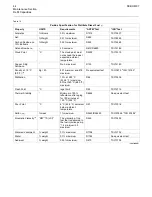
Table 15
Fuel Groups
Classi
fi
cation
Group 1
Preferred fuels
Full life of the
Product
Group 2
Permissible
fuels with an
appropriate fuel
additive
These fuels
MAY cause
reduced
engine life and
performance
Group 3
Permissible
fuels with an
appropriate fuel
additive
These fuels
WILL cause
reduced
engine life and
performance
Group 4
Biodiesel
Group 1 Speci
fi
cations (Preferred Fuels)
This group of fuel speci
fi
cations is considered
acceptable:
•
EN590 DERV Grade A, B, C, E, F, Class, 0, 1, 2,
3, and 4
•
“BS2869 Class A2” Off-Highway Gas Oil Red
Diesel
•
“ASTM D975”, Class 1D , and Class 2D
•
“JIS K2204 Grades 1,2,3 and Special Grade 3”
This grade of fuel must meet the minimum lubricity
requirements that are stated in table 14.
Note:
The use of LSD fuel and the use of ULSD
fuel is acceptable provided that the fuels meet the
minimum requirements that are stated in table 14.
The lubricity of these fuels must not exceed wear
scar diameter of 0.52 mm (0.0205 inch). The lubricity
test must be performed on a HFRR, operated at
60 °C (140 °F). Refer to “ISO 12156-1 ”. By using the
test methods “ASTM D5453, ASTM D2622, or ISO
20846 ISO 20884”, the content of sulfur in LSD fuel
must be below 500 PPM 0.05%. By using the test
methods “ASTM D5453, ASTM D2622, or ISO 20846
ISO 20884”, the content of sulfur in ULSD fuel must
be below 15 PPM 0.0015%.
Group 2 Speci
fi
cations (Permissible
Fuels)
This group of fuel speci
fi
cations is considered
acceptable, but only with an appropriate fuel additive,
but these fuels MAY reduce the engine life and
performance.
•
“MIL-DTL-83133E NATO F34 (JP-8)”
•
“MIL-DTL-83133E NATO F35 ”
•
“MIL-DTL-5624U NATO F44 (JP-5)”
•
“MIL-DTL-38219D (USAF) F44 JP-7”
•
“NATO F63”
•
“NATO XF63”
•
“ASTM D1655 JET A”
•
“ASTM D1655 JET A1”
Note:
These fuels are only acceptable provided that
these fuels are used with an appropriate fuel additive.
These fuels must meet the requirements that are
stated in table 14. Fuel samples should be analyzed
for the compliance. These fuels MUST NOT exceed
lubricity wear scar diameter of 0.52 mm (0.0205 inch).
The fuel lubricity test must be performed on a
HFRR, operated at 60 °C (140 °F). Refer to “ISO
12156-1 ”. Fuels must have minimum viscosity of
1.4 centistokes that is delivered to the fuel injection
pump. Fuel cooling may be required in order to
maintain minimum viscosity of 1.4 centistokes that is
delivered to the fuel injection pump.
Group 3 Speci
fi
cations (Permissible
Fuels)
This group of fuel speci
fi
cation must be used only
with the appropriate fuel additive. This fuel WILL
reduce engine life and performance.
“JIS 2203#1 and #2 Toyu”
Note:
These fuels are only acceptable provided that
these fuels are used with an appropriate fuel additive.
These fuels must meet the requirements that are
stated in table 14. Fuel samples should be analyzed
for the compliance. These fuels MUST NOT exceed
lubricity wear scar diameter of 0.52 mm (0.0205 inch).
The fuel lubricity test must be performed on a
HFRR, operated at 60 °C (140 °F). Refer to “ISO
12156-1 ”. Fuels must have minimum viscosity of
1.4 centistokes that is delivered to the fuel injection
pump. Fuel cooling may be required in order to
maintain minimum viscosity of 1.4 centistokes that is
delivered to the fuel injection pump.
Group 4 Biodiesel
Biodiesel is a fuel that can be de
fi
ned as mono-alkyl
esters of fatty acids. Biodiesel is a fuel that can
be made from a variety of feedstock. The most
commonly available biodiesel in europe is Rape
Methyl Ester (REM). This biodiesel is derived from
rapeseed oil. Soy Methyl Ester (SME) is the most
common biodiesel in the United States. This biodiesel
is derived from soybean oil. Soybean oil or rapeseed
oil are the primary feedstocks. These fuels are
together known as Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAME).