OMAP
TM
4 PandaBoard System
Reference Manual
Revision 0.4
September 22, 2010
DOC-21010
Page 17 of 83
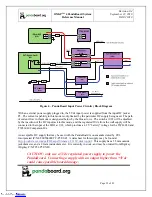
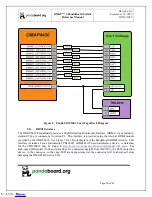
2.2
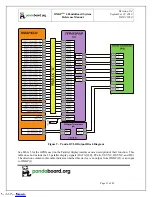
System Clock Distribution
The OMAP4430 PandaBoard implements a 38.4 MHz 1.8V CMOS square-wave oscillator that directly
drives the FREF_SLICER_IN input (ball AG8) of the OMAP4430 processor and the MCLK input to the
TWL6040 Audio Companion IC. This clock is used as an input to the PLLs within the OMAP4430
processor so that it can generate all the internal clock frequencies required for system operation.
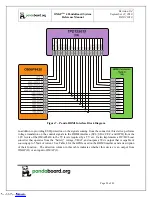
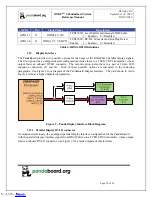
2.3
OMAP4430 Processor
The heart of PandaBoard is the OMAP4430 processor. The OMAP4430 high-performance multimedia
application device is based on enhanced OMAP™ architecture and uses 45-nm technology. For more
information, refer to the OMAP4430 Technical Reference Manual (TRM).The architecture is designed to
provide best-in-class video, image, and graphics processing sufficient to various applications. The device
supports the following functions:
•
Streaming video up to full high definition (HD) (1920 × 1080 p, 30 fps)
•
2-dimensional (2D)/3-dimensional (3D) mobile gaming
•
Video conferencing
•
High-resolution still image (up to 16 Mp)
The device supports high-level operating systems (OSs) such as:
•
Windows™ CE, WinMobile™
•
Symbian OS™
•
Linux®
•
Palm OS™
The device is composed of the following subsystems:
•
Cortex™-A9 microprocessor unit (MPU) subsystem, including two ARM® Cortex-A9
cores
•
Digital signal processor (DSP) subsystem
•
Image and video accelerator high-definition (IVA-HD) subsystem
•
Cortex™-M3 MPU subsystem, including two ARM Cortex-M3 microprocessors
•
Display subsystem
•
Audio back-end (ABE) subsystem
•
Imaging subsystem (ISS), consisting of image signal processor (ISP) and still image
coprocessor (SIMCOP) block
•
2D/3D graphic accelerator (SGX) subsystem
•
Emulation (EMU) subsystem
The device includes state-of-art power-management techniques required for high-performance mobile
products. Comprehensive power management is integrated into the device. The device also integrates:
•
On-chip memory
•
External memory interfaces
•
Memory management
•
Level 3 (L3) and level 4 (L4) interconnects
•
System and connecting peripherals
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from
Downloaded from