Clara
32
Version 2.0 rev 24 Mar 2015
Vertical Binning
In Vertical Binning, charge from two or more rows of the CCD-chip is moved down into the shift register before the
charge is read out. The number of rows shifted depends on the binning pattern you have selected. Thus, for each
column of the CCD-chip, charge from two or more vertical elements is ‘summed’ into the corresponding element of the
shift register. The charge from each of the pixels in the shift register is then shifted horizontally to the output node of the
amplifier and read out.
Variants of Vertical Binning are used to affect a variety of binning patterns and they are as follows:
•
Single-Track
: charge is vertically binned and read out from a number of complete, adjacent rows of pixels on
the CCD-chip. The rows form a single track across the full width of the CCD-chip. A value is taken for each
column in the track.
•
Multi-Track
: Multi-Track mode differs from Single-Track in that you may now define two or more tracks from
which to read out charge. In processing terms, each track is treated as in Single-Track above.
•
Full Vertical Binning (FVB)
: charge from each complete column of pixels on the CCD is moved down and
summed into the shift register and the charge is then shifted horizontally one pixel at a time from the shift
register into the output node - in effect a value is read out for each complete column of the CCD-chip.
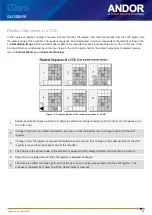
The example below illustrates readout of data from adjacent tracks, each track comprising two binned rows of the CCD-
chip.
Figure 15: Vertical Binning of two rows
1
Exposure to light causes a pattern of charge (an electronic image) to build up on the frame (or Image Area) of
the CCD-chip.
2
Charge in the frame is shifted vertically by one row, so that the bottom row of charge moves down into the
shift register.
3
Charge in the frame is shifted vertically by a further row, so that the next row of charge moves down into the
shift register, which now contains charge from two rows - i.e. the charge is vertically binned
4
Charge in the shift register is moved horizontally by one pixel, so that charge on the endmost pixel of the shift
register is moved into the output node of the amplifier.
5
The charge in the output node of the amplifier is passed to the analog-to-digital converter and is read out.
6
Steps 4 & 5 are repeated until the shift register is empty. The process is repeated from Step 2 until the whole
frame is read out.
GLOSSARY